User Manual - ePowerControl
PV/Diesel/Grid integration Controller
Product installation instructions for:
- ePowerControl HFS-M & HFS-L
- ePowerControl ZE 3000
Table of Contents
General information
About this manual
This manual provides users with all the essential information needed to install, configure, and operate the ePowerControl ZE, ePowerControl SD, and ePowerControl HFS products by Elum Energy. It includes product details, safety guidelines, installation procedures, and configuration instructions.
For information on ePowerLog DataLogger, please refer to its dedicated user manual. For details regarding ePowerControl MC and ePowerControl PPC, please contact the Elum team.
Intended audience
- EPCs involved in the deployment of new hybrid PV/Genset systems or grid-tied PV systems.
- EPCs integrating PV/Genset solutions into existing genset-based power systems.
- Professionals responsible for the design, installation, and maintenance of hybrid power systems.
The following symbols are used to highlight key information throughout this document:
⚠️ Warning
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation that could lead to serious injury or death. This symbol is used to highlight precautionary measures and safety guidelines that must be followed.
ℹ️️ Notes
Provides general information or useful tips to help the user during installation, configuration, or operation.
⚠️ Before installing the ePowerControl, carefully read this manual to prevent personal injury and avoid equipment damage.
Glossary
| APN address | A gateway that connects a GSM, GPRS, 3G, or 4G mobile network to another computer network. |
| AWG (12 wires) | American wire gauge : A standard unit for measuring the diameter of electrical wires. |
| CT | Current Transducers: A device that detects electric current in a wire and generates a proportional signal. |
| DHCP mode | Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol: A network protocol that automatically assigns IP addresses to devices. |
| DIN rail | A standardized metal rail used for mounting industrial control equipment inside enclosures or racks. |
| EMS | Energy Management System A system designed to monitor and/or control, and optimize energy usage in industrial and commercial environments. |
| EPC | Engineering, Procurement & Commissioning : A company responsible for the design, procurement, and installation of power systems. |
| I/O module | Input/Output module : A device that manages input and output signals between control systems and external devices. |
| ICMP | Internet Control Message Protocol : A network protocol used for diagnostic and error reporting in IP networks (e.g., Ping command). |
| LAN ports | Local Area Network : Physical connections for networking devices within a local network. |
| Local NEC rules | National Electrical Code: A standard for the safe installation of electrical wiring in various regions. |
| Modbus RTU | Communication protocol to connect a supervisory computer with a remote terminal unit (RTU) |
| Modbus TCP | Communication protocol to connect a supervisory computer with a remote terminal unit through Ethernet with a transmission control protocol (TCP) |
| OCPP | Open Charge Point Protocol for communication between electric vehicle charging stations and a central management system |
| RS-485 | Standard electrical characteristics of drivers and receivers in serial communications systems |
| SCADA | Supervisory control and data acquisition |
| SNMP | Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an Internet Standard protocol for collecting and organizing information about managed devices on IP networks and for modifying that information to change device behavior. |
| UDP ports | Ports for User Datagram Protocol |
| UPS | Uninterruptible Power Supply : A backup power system used to ensure continuous operation of the controller, preventing data loss or system shutdowns during power outages. |
Legal information
Elum SAS, headquartered at 9 rue d’Enghien – 75010 Paris, is registered with the Paris Trade and Companies Registry under number 817 860 083. The company specializes in the integration and distribution of monitoring and control panels for photovoltaic and hybrid energy systems, marketed under the brands “ePowerLog” and “ePowerControl”.
Elum ensures that its controllers and dataloggers comply with French quality standards, are designed and assembled in France, and meet all necessary technical and quality requirements.
Elum reserves the right to modify the content of this document as needed. In the event of any discrepancy between translated versions, the English version shall take
precedence.
Safety warnings
Elum ePowerControl products are electrical devices and should only be installed and operated by qualified personnel who are aware of the associated safety risks.
⚠️ Installation of meters
Voltage-carrying parts. Risk of heart attack, burns and other injuries. Disconnect the power supply and charge the device before installing the analyzer. Protect the terminals with covers. The energy analyser must be installed by qualified/approved personnel.
⚠️ Dangerous voltage
Do not touch the terminals for voltage and current measurement. Always connect grounding terminals. Do not disconnect the controller CT terminals. Be careful to protect the unit from electrostatic discharges during the installation.
ℹ️️ Internet access
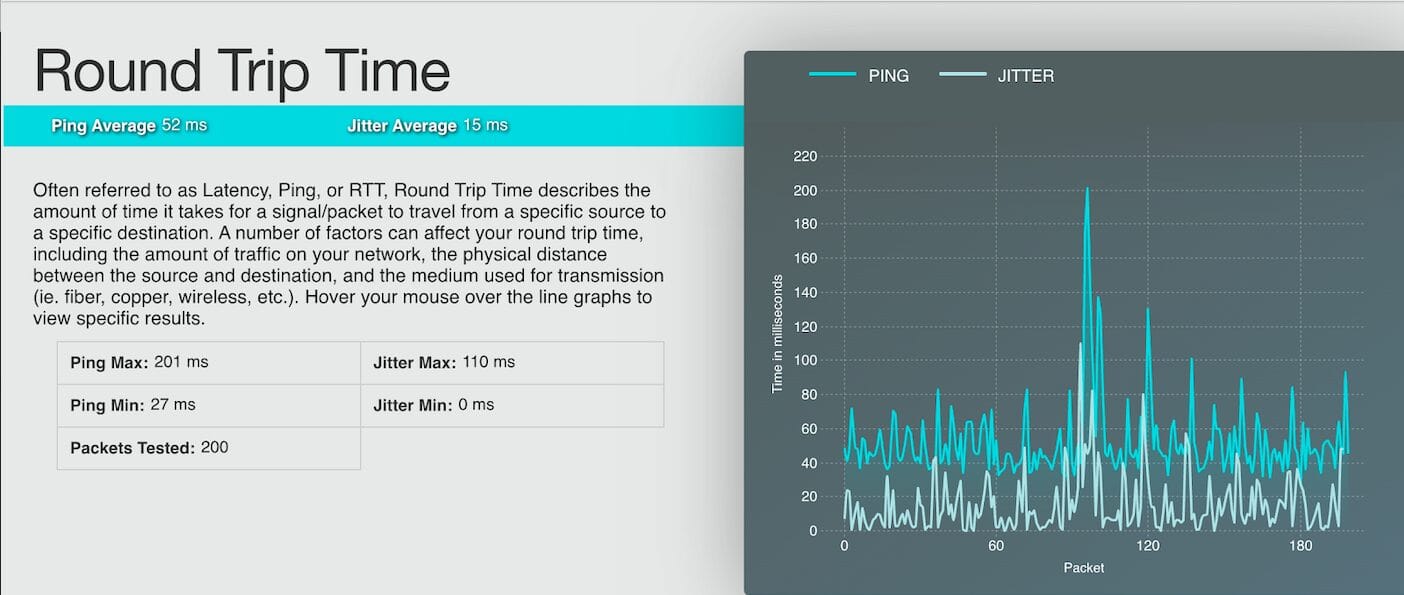
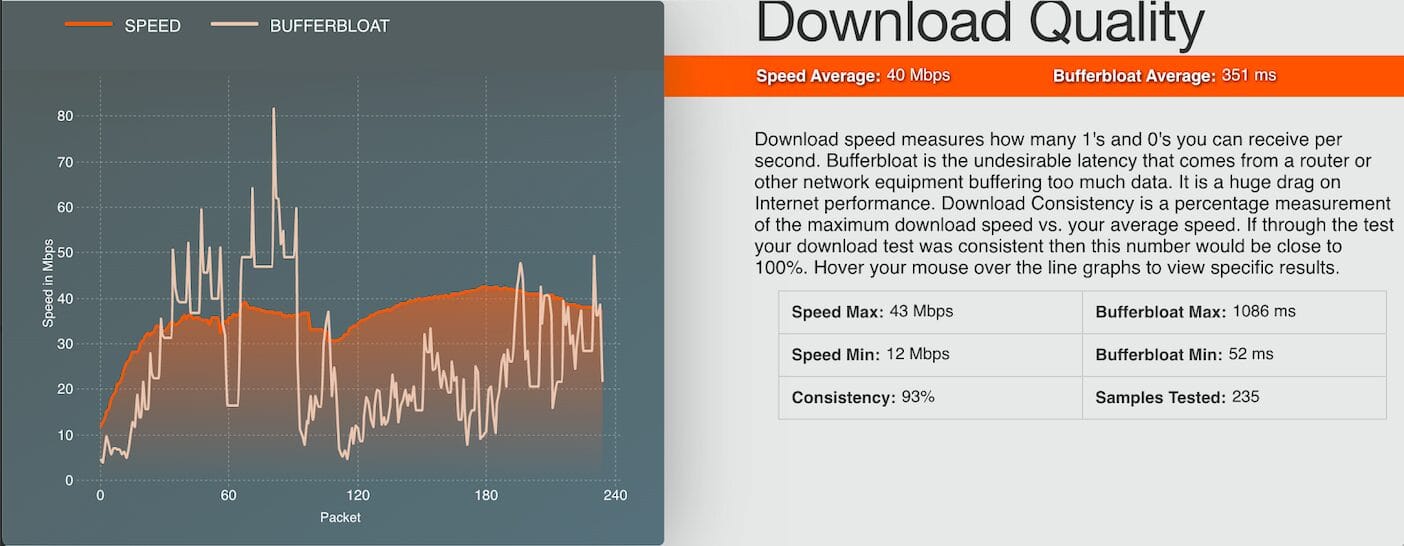
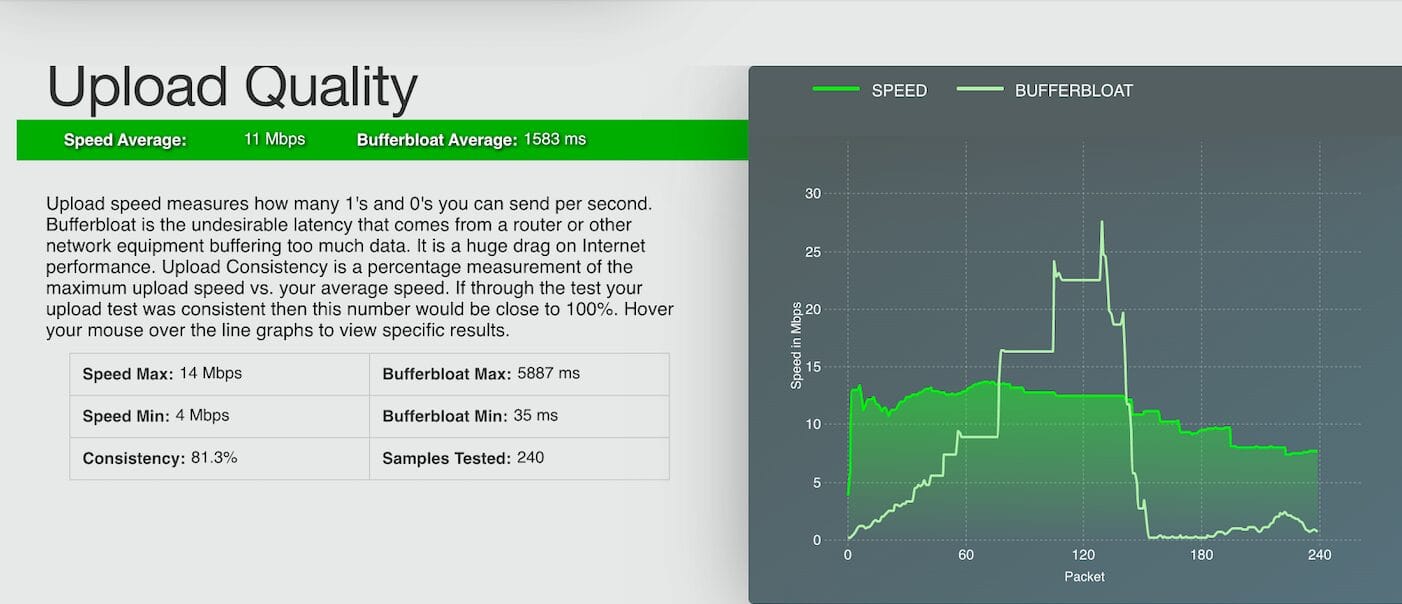
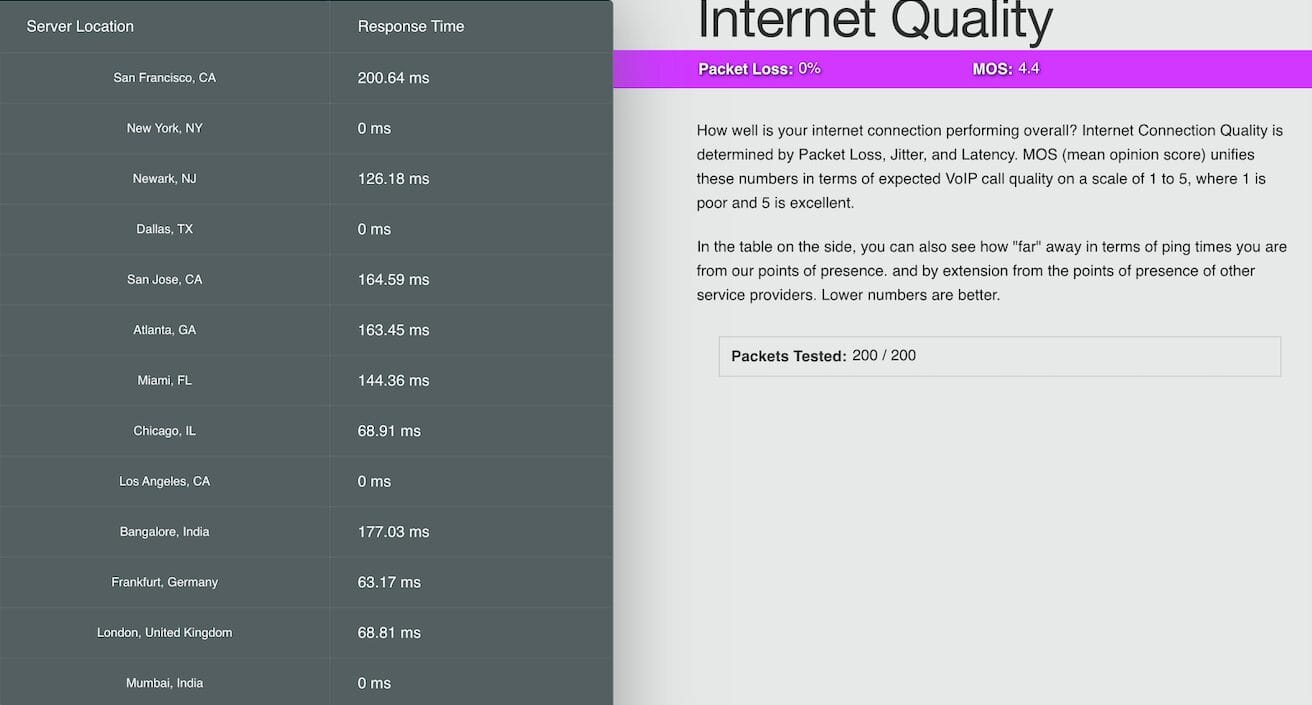
A stable internet connection is required to commission the ePowerControl controllers successfully. For more details, refer to Appendix C: Internet Speed Test.
ℹ️️ Monitoring and control features
Elum can only guarantee the monitoring and control of the site according to its product features once all of the equipment to be monitored have correctly been configured and connected to the controller.
⚠️ Reverse Power Protection (for the ePowerControl SD, HFS, MC and PPC)
The ePowerControl is NOT an electrical protection. It does not replace an adequate protection of diesel generators against power reversal, nor a properly configured/installed protection relay, nor a properly configured/installed genset controller integrating the reverse current protection functionality. If necessary, please install protection relays against reverse power.
Scope of supply
The ePowerControl Controller
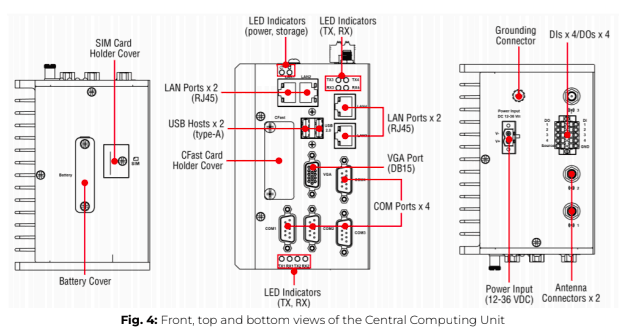
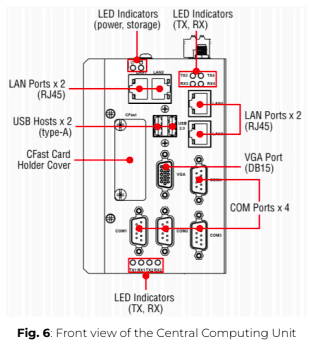
The ePowerControl is a ready-to-use solution that consists of a Central Computing Unit (CCU) and one or more satellites. The central unit is responsible for executing control algorithms and enabling remote communication with the Elum cloud via the Internet. Any additional options purchased by the client will already be integrated into the base station, ensuring seamless operation upon installation.
ℹ️️ For detailed specifications and technical information regarding the Central Computing Unit, please refer to the ePowerControl datasheet.
Additional equipment
Additional external equipment, such as weather sensors, I/O modules, and power meters, included in the purchase order will be delivered under the same terms as the controller. Some of these components may already be pre-installed within the ePowerControl cabinet, while others will require installation by the client. For further details on optional accessories and configurations, please refer to the Options section of this manual.
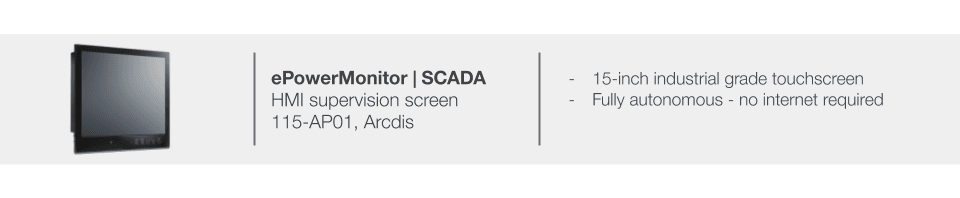
Monitoring platform – ePowerMonitor
Upon purchase of a subscription to the ePowerMonitor platform, and once all hardware components are installed, the internet connection is configured, and the commissioning tests are completed, Elum will provide the client with access credentials for the ePowerMonitor online platform. This access includes a User ID and Password, enabling remote monitoring and control of the system.
Operating modes
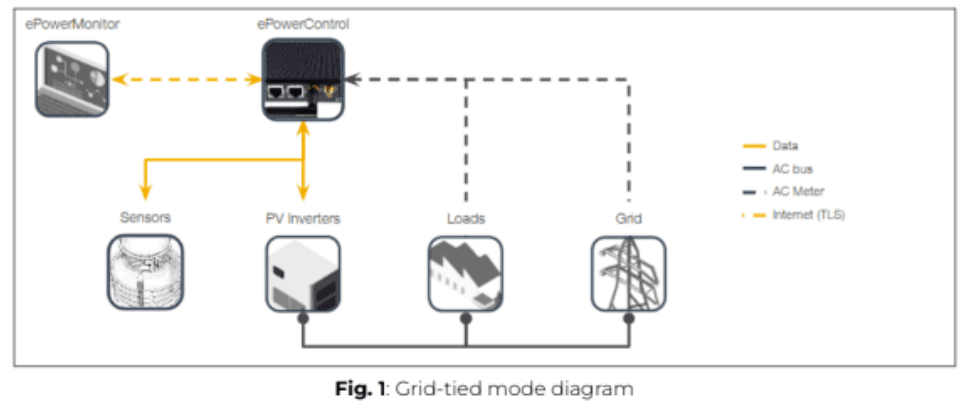
Grid-tied mode
The grid-tied mode refers to a power system that integrates PV and the grid, operating in a configuration similar to the one illustrated in Figure 1.
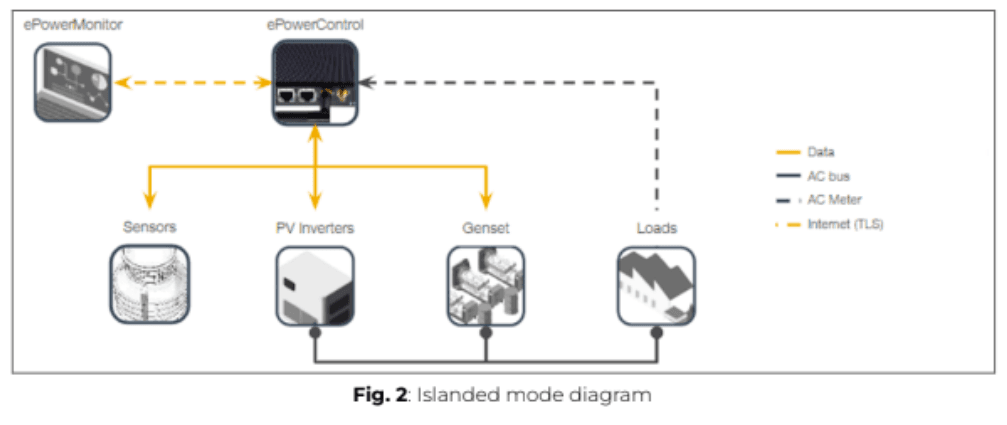
Islanded mode
The islanded mode refers to a PV + Genset power system operating without grid connection, as illustrated in Figure 2.
Back-up mode
The back-up mode refers to a power system configuration integrating PV, Genset, and Grid, ensuring continuous power supply by switching between sources as needed. The system operates as illustrated in the accompanying figure 3.

Commissioning overview
Before proceeding to the commissioning
Before initiating the commissioning process, Elum will provide the following essential documents:
- User Manual
- Datasheet
- Software delivery note
The ePowerControl controller is delivered with pre-installed Elum firmware, ensuring that it is ready for installation. The installation team must follow the step-by-step instructions provided in this manual to complete the autonomous commissioning of the controller.
The entire system configuration can be performed on-site, and all necessary setup details are included within this document.
ℹ️️ Equipment first integration by Elum
For the integration of new equipment by Elum, the Operations team must be notified at least 15 days prior to deployment. Failure to do so may result in limited availability of Elum engineers for assistance, and their full support cannot be guaranteed.
⚠️ PV injection precaution
During the deployment process, PV injection must remain shut down. Elum cannot be held responsible for any damage caused by uncontrolled PV injection during the commissioning process. It is the responsibility of the installation team to ensure that proper precautions are taken before proceeding.
Deployment steps
| Step 1 | Read the User Manual |
| Step 2 | Plan the communication architecture |
| Step 3 | Wire the slave devices |
| Step 4 | Connect and configure all non-Elum equipment:
|
| Step 5 | Wire and install the ePowerControl |
| Step 6 | Configure the ePowerControl online with Elum Configuration:
|
| Step 7 | Functional tests |
| Step 8 | (Optional) access to ePowerMonitor |
Step 2: Communication Architecture Plan
Objectives
Before commissioning, a clear communication plan must be established to prevent any network-related issues. The design of the network should take into account wiring limitations, communication protocol compatibility, and the configuration requirements of each device to ensure seamless integration.
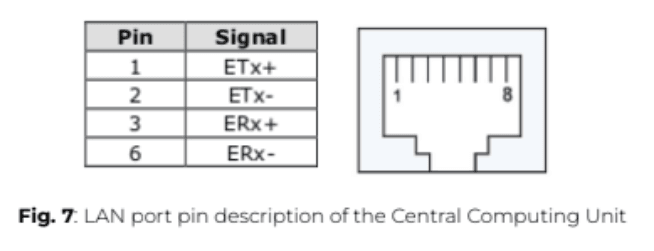
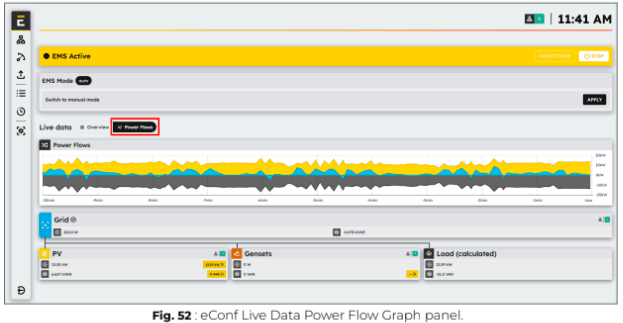
ℹ️️ LAN port No. 4 of the Central Computing Unit is exclusively for connecting your computer to access eConf; it cannot be used for monitoring or control purposes.
RS485 Constraints: Configuring Slave ID Addresses
To ensure stable communication via RS485 (Modbus RTU), the following rules must be followed:
ℹ️️ Each device must have a unique Slave ID to avoid address conflicts.
ℹ️️ All devices connected to the same serial port must use the same communication protocol and have matching parameters, including baud rate, parity, byte size, and stop bits.
ℹ️️ The Modbus RTU protocol allows up to 32 devices to be connected to a single serial communication port.
ℹ️️ Limits
The maximum cable length for RS485 communication must not exceed 1000 meters to ensure signal integrity.
Ethernet Constraints: Configuring IP Addresses
For proper Ethernet communication, the following guidelines must be observed:
ℹ️️ Each device must have a unique IP address within the network.
- All devices must be within the same subnet as the Elum Explorer to allow seamless data exchange.
- The subnet range 192.168.4.XX is reserved for LAN port 2 and must not be used for other devices.
ℹ️️ All devices should be configured with the Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0 to maintain proper network segmentation and communication stability.
ℹ️️ Limits
The maximum Ethernet cable length must not exceed 100 meters to prevent signal degradation and ensure reliable communication
Example
Table 1: Communication Architecture Plan Example
| Slave Reference | Slave Reference | Protocol | Slave IP address | Slave ID | Byte Size | Stop Bit | Parity | Stop Bit |
| Inverter n°1 | SMA STP 25000 TL | Modbus TCP | 192.168.3. 200 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Inverter n°2 | SMA STP 25000 TL | Modbus TCP | 192.168.3. 201 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Inverter n°3 | SMA STP 25000 TL | Modbus TCP | 192.168.3. 202 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Inverter n°3 | SMA STP 25000 TL | Modbus TCP | 192.168.3. 203 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Grid Meter | EM330-DIN .AV5.3.H.S1. X, Carlo Gavazzi | Modbus RTU | – | 2 | 9600 | 8 | No | 1 |
| Load Meter | EM330-DIN .AV5.3.H.S1. X, Carlo Gavazzi | Modbus RTU | – | 1 | 9600 | 8 | No | 1 |
Step 3: Wire the slave devices
Connecting RS485 Devices
To enable the ePowerControl to monitor external devices via RS485, a physical connection must be established. The ePowerControl functions as the master of the communication bus, while all connected equipment act as slaves. Each slave device must be properly configured to ensure seamless communication using the Modbus RTU protocol.
Central Computing Unit serial ports
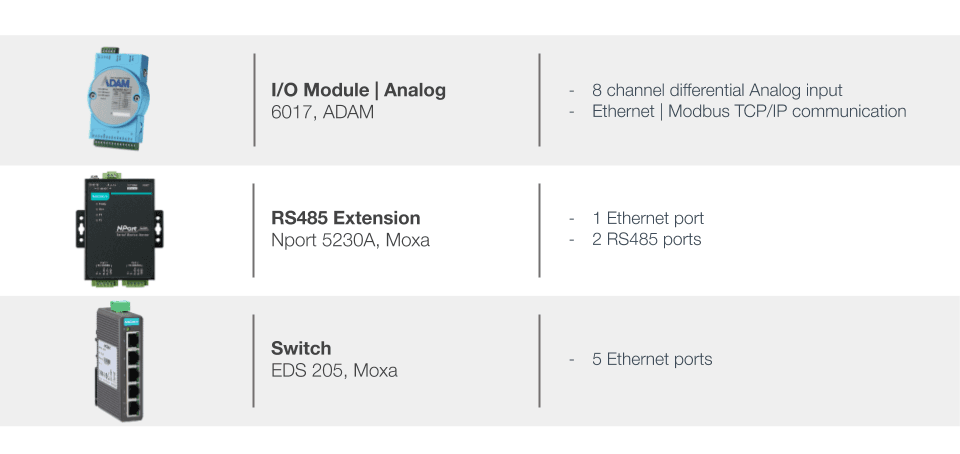
RS485-compatible devices can be connected to Serial Port 1, 2, 3 or 4 on the ePowerControl Central Computing Unit using shielded twisted pair connectors. If an RS485 Extension Module is provided by Elum, its serial ports 1, 2, 3 or 4 can also be used for device connections.
For specific wiring and configuration details related to third-party hardware, please refer to the manufacturer’s documentation to ensure compatibility and correct setup.
The table below provides the pin configuration for the ePowerControl communication ports, used to connect RS485-compatible devices to the ePowerControl Central Computing Unit. Proper wiring and adherence to these pin assignments are crucial to ensure stable data transmission and device monitoring.

ℹ️️ For correct RS485 wiring, ensure that Pin 3 (Data B+) and Pin 4 (Data A-) are connected using a shielded twisted pair cable to prevent interference. Pin 5 (GND) should also be connected to maintain signal integrity.

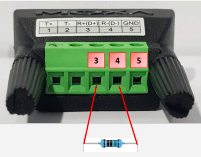
RS-485 wiring guidelines
Proper wiring of the RS-485 serial line is essential for ensuring reliable data transmission between the ePowerControl and connected devices.
Follow these guidelines to minimize interference and maintain stable communication:
- Daisy chaining connections
1. Pin 3 (DataB +) of the serial port should be connected in a daisy-chain with all DataB (+) ports of the connected devices
2. Pin 4 (DataA -) of the serial port should be connected in a daisy-chain with all DataA (-) ports of the connected devices.
3. Pin 5 (GND) should be connected in a daisy-chain with all GND ports of the connected devices. - Cable selection & Organization
1. Use twisted-pair cables for DataB (+) and DataA (-) to reduce electromagnetic interference
2. To simplify wiring and avoid errors, maintain a consistent color scheme (e.g., red for DataB (+), blue for DataA (-), and black for GND).
Termination of data wires
To prevent signal reflections and data errors, termination resistors must be installed:
- A 120 Ohm resistor should be placed at each end of the RS-485 communication line, connecting DataB (+) and DataA (-).
- The resistance value must be compatible with the impedance of the communication cable used.
Shielding
RS-485 wiring recommendations:
For RS-485 communication lines, it is recommended to use shielded wires to minimize interference.
- The shielding should be electrically continuous along the entire serial line and must be connected to the GND wire of the RS-485 circuit at the controller (pin 5).
- To prevent ground loops, avoid multiple shield-to-ground connections. The only grounding point should be at the controller, where it connects to the GND wire.
- The use of unshielded data wires should be minimized, as they are more susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI).
RS-485 usage limitations:
- A maximum of 10 devices can be connected to a single RS-485 port using a daisy-chain configuration.
- The total cable length between the controller and the farthest external device must not exceed 1 km when using RS-485-compatible cables.
⚠️ Failure to adhere to the RS-485 wiring guidelines, including the use of termination resistors, proper grounding, and adequate shielding can lead to unstable communication, reduced performance, and even potential equipment damage.
⚠️ To maintain signal integrity, shield continuity must be ensured throughout the entire communication line. This requires dedicated third-party hardware for shield connections, with the shield being grounded at a single point to prevent ground loops.
ℹ️️ For RS-485 lines exceeding 100 meters, the installation of a 120 Ohm termination resistor is strongly recommended. This resistor should be placed between pin 3 and pin 4 on the RS-485 port of the Central Computing Unit, ensuring stable data transmission over long distances.
Connecting Ethernet Devices
To enable the ePowerControl to monitor Ethernet-based equipment, a physical Ethernet connection must be established. The ePowerControl acts as the master of the communication network, while all connected devices function as slaves. The controller communicates via Modbus TCP/ IP depending on the protocol supported by the connected devices.
Central Computing Unit LAN ports
To connect power units, sensors, or other Ethernet-compatible devices, use an
Ethernet-male to Ethernet-male cable and connect it to the LAN ports 1, 2 or 3 on the ePowerControl module.
- If no Ethernet switch is used, devices communicating via Modbus TCP
or SNMP must be directly connected to one of the 3 LAN ports on the Controller (1, 2 or 3). - If an Ethernet switch is used, all Modbus TCP devices should be connected to any of the available ports on the switch. One of the Ethernet switch ports must then be connected to the ePowerControl, ensuring seamless data transmission.
The 3 10/100 Mbps Ethernet ports of the Central Computing Unit and the switches provided by Elum use RJ45 connectors.
Wiring
The wiring of the Ethernet line should be done by connecting each of the Slaves to the ePowerControl using an RJ45 cable.
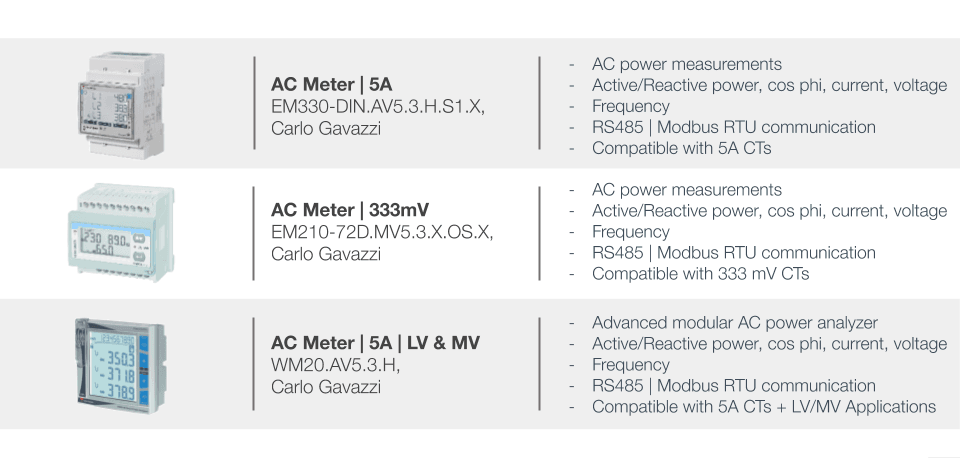
Wiring an AC Meter | 5A provided by Elum
Materials required
The installation and wiring of an AC Meter | 5A provided by Elum require the following components:
- Circuit protection: For each phase, use the smallest available breakers or rated fuse taps according to local NEC regulations. Typically, a 15A circuit breaker or a single multipole breaker is used, depending on the number of phases.
- Wiring: Use black, red, and white stranded AWG 12 wire, ensuring a thermal resistance of at least 75°C. The wire length should be determined based on the installation location. For three-phase installations, an additional blue wire is required. The insulation rating of the wire must be greater than the maximum voltage inside the panel.
- Other materials:
○ Electrical tape for insulation.
○ Conduit and couplings as needed.
○ Mounting and wire organization hardware to ensure a neat and secure installation.
○ Outdoor-rated enclosure (if the meter is installed outside) to protect against environmental conditions.
Safety warnings
⚠️ To ensure a safe and proper installation, always follow the wiring diagrams and CT selection guidelines provided in this manual.
To reduce the risk of electric shock and prevent damage to the equipment:
- Do not connect the device to a circuit that operates at more than 277 Vrms to neutral.
- Always disconnect circuits from the building’s power distribution system before installing or servicing the power meter or attached current transformers (CTs).
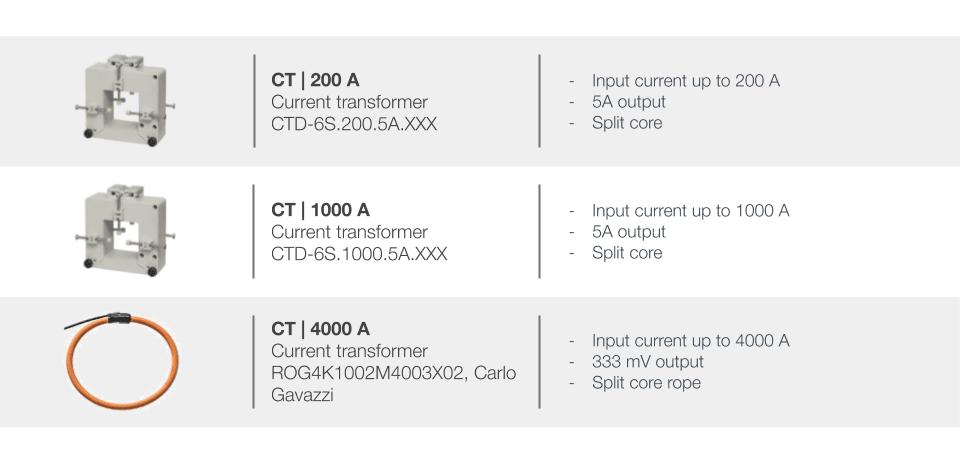
- Only use authorized 5A CTs with this device to maintain accurate measurement and ensure safe operation.
Installation location
The power meter should be installed near the low-voltage distribution panel, ensuring easy access to connections for the grid, load, and genset (refer to the application overview for guidance). A 10A circuit breaker must be installed for each phase, positioned close to the meter and within easy reach of the operator. These breakers must be clearly labeled as the disconnecting devices for the power meter to allow quick identification and access.
Since the power meter is a listed device, it must be housed inside a suitable enclosure that meets the environmental requirements of the installation site:
- For indoor installations, a standard electrical cabinet is sufficient.
- For outdoor installations, a weatherproof, outdoor-rated enclosure is required to protect against moisture, dust, and direct sunlight.
When selecting the installation location, ensure that the power meter is not exposed to direct sunlight or extreme environmental conditions.
Device overview
Installation steps
- Place the required breaker(s) in the power distribution panel, ensuring access to all phases of the system.
- Open the breakers to ensure there is no power on the breaker contacts before proceeding with the installation.
- Securely mount the power meter inside a suitable enclosure near the power
distribution panel. - Ensure the enclosure is appropriate for the installation environment (e.g., outdoor-rated enclosures for external installations).
- Wiring the Power Meter and CTs:
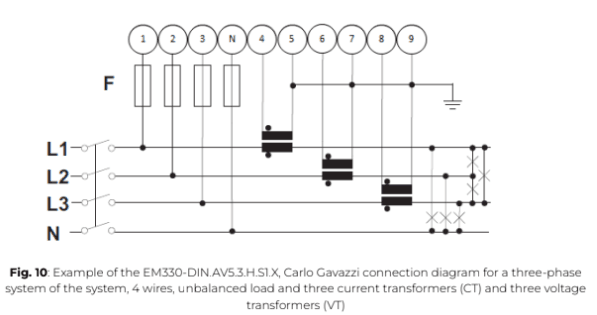
a. Follow the wiring diagram corresponding to the site’s system layout to properly connect the power meter.
b. For a three-phase system with a 4-wire unbalanced load, connect the three current transformers (CTs) as specified in the installation diagram.
c. Ensure the stickers on the CTs are correctly oriented toward the measured current flow direction to avoid incorrect readings.
d. If the CT wires need to be adjusted in length, ensure they are securely connected without compromising signal integrity.
ℹ️️ The main voltage must not exceed 400V, and the CTs must always have 5A secondary current.
ℹ️️ The power supply should be 65-400V AC, 50Hz.
⚠️ The auxiliary power supply on the meter ensures it remains powered regardless of whether the plant is running on the grid or gensets.
Power meters responsible for monitoring the grid, load, or gensets should never be turned off, as this could trigger a fail-safe mode in the ePowerControl, leading to curtailed PV production.
7. Close the newly installed breakers to energize the power meter. Within a few seconds, the screen should illuminate, displaying the measurement page to confirm proper operation.
8. Once the power meter is successfully powered on, you can continue with the configuration and parameter setup to align with the system’s operational
requirements.
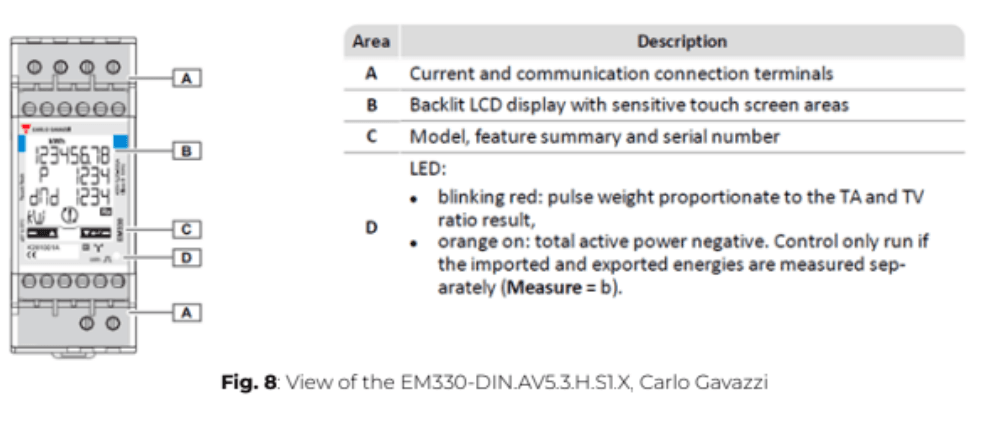
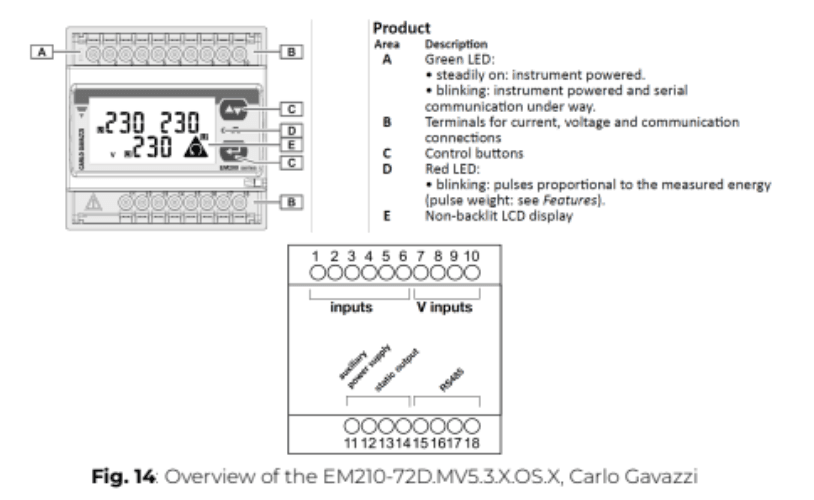
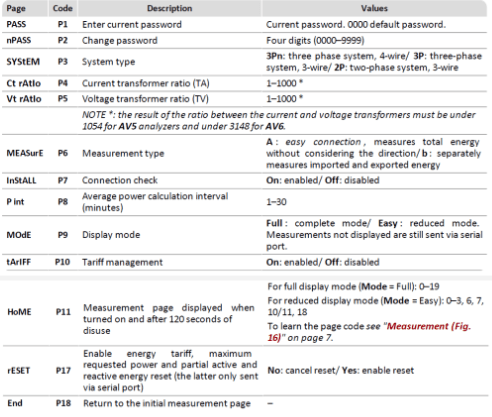
ℹ️️ When installing a EM210-72D.MV5.3.X.OS.X, Carlo Gavazzi the critical parameters to be set are listed below:
SYStEM, System type: To be set according to the site design.
SEnSOr , CT type: To be set according to the CTs used with the power meter. As an example, when installing the power meter with Rogowski coil CTs, the type should be set to roG
Ct Prin, Current transformer maximum current input: To be set according to the CTs used with the power meter. As an example, when installing the power meter with Rogowski coil 4000A, the type should be set to 4,00k.
Vt rAtIo, Voltage transformer ratio: To be set according to the VTs used with the power meter. You can obtain this ratio by dividing the primary voltage by the secondary voltage. As an example, when installing the power meter using no VTs, the ratio should be set to 1.
APPLiC, Measurement application: To be set to “E”.
AddrESS, Modbus address: To be set according to your ID plan
⚠️ The result of the ratio between the current and voltage transformers must be under 1054.
⚠️ It is critical that the measurement type was correctly set up to “b” for the zero export control feature. If the power meter was not correctly set up, Elum cannot guarantee any reliability on the zero export feature and will not be taken responsible if some energy is exported to the grid.
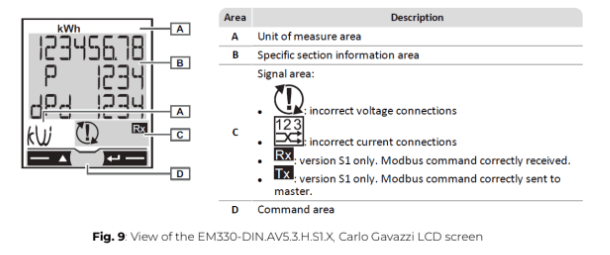
ℹ️️ Instructions to use the power meter and navigate through the different menus.
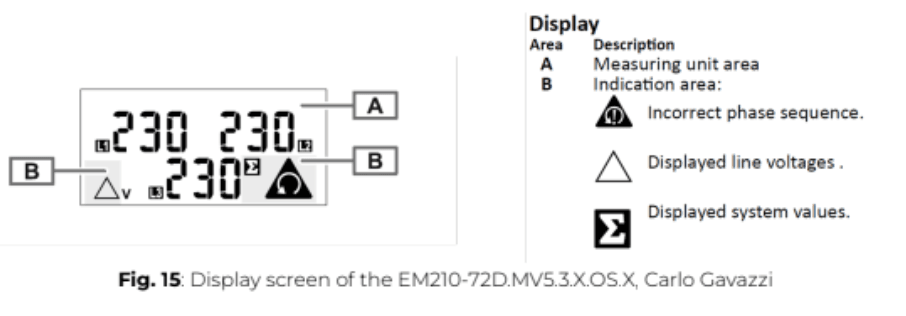
Measurement pages displayed by default when turned on. Pages are characterized by the reference unit of measure. The initial measurement page set is displayed after 120 s of disuse.
ℹ️️ Parameters description
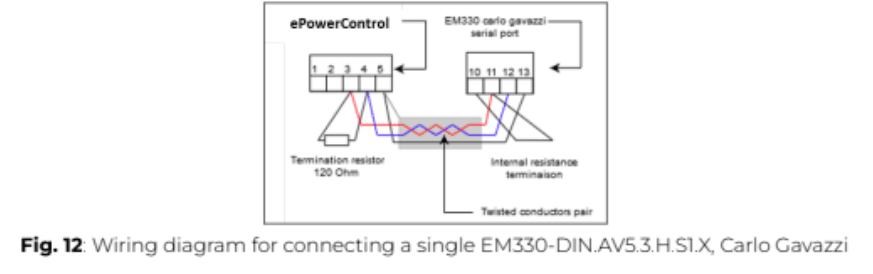
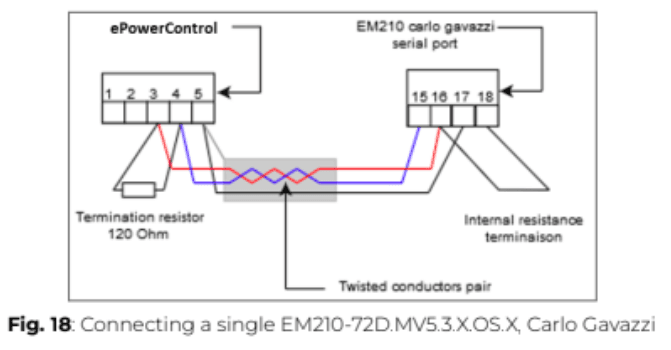
9. Proceed to the communication wiring of the power meter as described below. Connect the power meter to one of the serial ports of the Central Computing Unit using a shielded twisted-pair RS485 connector and a Cat 5 cable.
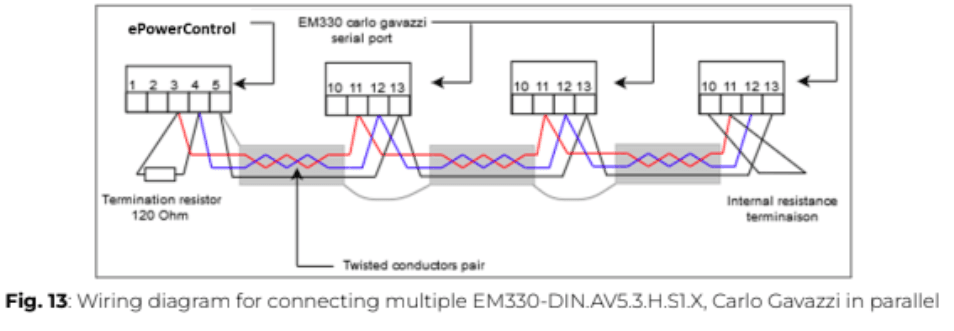
Additional RS485 power meters should be connected in parallel, with the serial output terminated only on the last device by connecting terminals B+ and T. For connections over 1000 meters or networks with more than 160 devices, a signal repeater must be used.
⚠️ The continuity of the shielding must be ensured throughout the communication cable, and the ground must be connected at a single point. The total length of the cable must not exceed 1000m.
10. Label the newly installed breakers as “Power Meter Disconnect” so they can be easily identified if the device needs to be power-cycled or turned off.
Wiring an AC Meter | 333mV provided by Elum
Materials required
- Circuit protection: For each phase, use the smallest available breakers or rated fuse taps according to local NEC regulations. Typically, a 15A circuit breaker or a single multipole breaker is used, depending on the number of phases.
- Wiring: Use black, red, and white stranded AWG 12 wire, ensuring a thermal resistance of at least 75°C. The wire length should be determined based on the installation location. For three-phase installations, an additional blue wire is required. The insulation rating of the wire must be greater than the maximum voltage inside the panel.
- Other materials:
○ Electrical tape for insulation.
○ Conduit and couplings as needed.
○ Mounting and wire organization hardware to ensure a neat and secure installation.
○ Outdoor-rated enclosure (if the meter is installed outside) to protect against environmental conditions.
Safety warnings
⚠️ To ensure a safe and proper installation, always follow the wiring diagrams and CT selection guidelines provided in this manual.
To reduce the risk of electric shock and prevent damage to the equipment:
- Do not connect the device to a circuit that operates at more than 277 Vrms to neutral.
- Always disconnect circuits from the building’s power distribution system before installing or servicing the power meter or attached current transformers (CTs).
- Only use authorized 5A CTs with this device to maintain accurate measurement and ensure safe operation.
Installation location
The power meter should be installed near the low-voltage distribution to ensure easy access to the grid, load, and genset connections (see application overview). A 10A circuit breaker per phase must be installed close to the device and within easy reach of the operator. These breakers must be clearly labeled as the disconnecting device for the power meter.
As a listed device, the power meter must be housed in a suitable enclosure rated for its installation environment. For outdoor installations, a weather-resistant, outdoor-rated enclosure is required to protect against environmental conditions. The installation location should be shielded from direct sunlight and harsh elements to ensure long-term reliability and accuracy.
Device overview
Installation steps
- First, install the breaker(s) in the power distribution panel, ensuring they provide access to all phases.
- Before proceeding, open the breakers to ensure no power is present on the breaker contacts.
- Next, mount the power meter inside a suitable enclosure near the power distribution panel, ensuring easy access for wiring and maintenance.
- Proceed with the wiring of the power meter and CTs, following the wiring diagram corresponding to the site system layout. For a three-phase system with a 4-wire unbalanced load, connect the three current transformers (CTs) as specified. Ensure that the CT stickers are correctly oriented toward the measured current flow. If CT wires need to be shortened or extended, make sure they are properly connected to maintain signal integrity.
ℹ️️ The main voltage must not exceed 400V, and the CTs must always have a 333mV output.
5. Proceed with the power supply wiring of the power meter as specified. The power supply should be 65-400V AC, 50Hz.
ℹ️️ The power supply should be 65-400V AC, 50Hz.
⚠️ The auxiliary power supply on the meter ensures it remains powered regardless of whether the plant is running on the grid or gensets. Power meters responsible for monitoring the grid, load, or gensets should never be turned off, as this could trigger a fail-safe mode in the ePowerControl, leading to curtailed PV production.
6. Once the wiring is complete, close the newly installed breakers. Within a few seconds, the power meter should turn on, and its screen will display the measurement page.
7. At this point, you can proceed with the parameter setup of the power meter.
ℹ️️ When installing a EM210-72D.MV5.3.X.OS.X, Carlo Gavazzi the critical
parameters to be set are listed below:
SYStEM, System type: To be set according to the site design.
SEnSOr , CT type: To be set according to the CTs used with the power meter. As an example, when installing the power meter with Rogowski coil CTs, the type should be set to roG
Ct Prin, Current transformer maximum current input: To be set according to the CTs used with the power meter. As an example, when installing the power meter with Rogowski coil 4000A, the type should be set to 4,00k.
Vt rAtIo, Voltage transformer ratio: To be set according to the VTs used with the power meter. You can obtain this ratio by dividing the primary voltage by the secondary voltage. As an example, when installing the power meter using no VTs, the ratio should be set to 1.
APPLiC, Measurement application: To be set to “E”.
AddrESS, Modbus address: To be set according to your ID plan
⚠️ The combined ratio of the current and voltage transformers must not exceed 1054.
⚠️ It is essential to set the measurement application to “E” for the zero export control feature. If this setting is incorrect, Elum cannot guarantee the reliability of zero export control and will not be responsible for any unintended energy export to the grid.
ℹ️️ For instructions on using the power meter and navigating through its menus, refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
When powered on, the default measurement pages will be displayed, each showing a reference unit of measure. If no interaction occurs, the initial measurement page will automatically reappear after 120 seconds of inactivity.
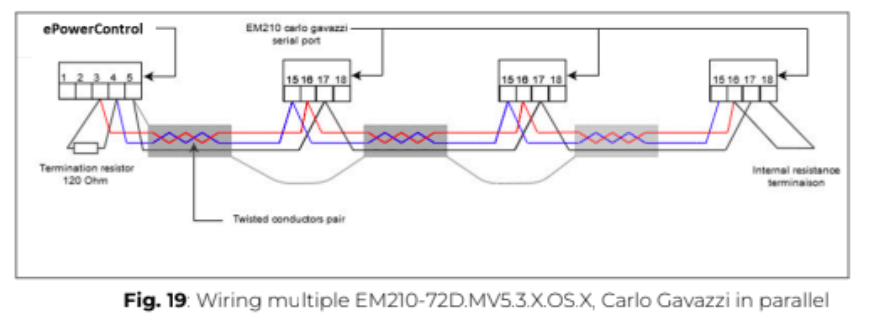
8. To establish communication, connect the power meter to one of the serial ports of the Central Computing Unit (CCU) using a shielded twisted-pair RS485 connector and a Cat 5 cable.
Additional RS485 power meters must be connected in parallel (daisy-chained). The serial output should only be terminated on the last device in the network by connecting terminals B+ and T.
The total cable length must not exceed 1000 meters to ensure reliable communication.
⚠️ The shielding continuity must be maintained throughout the entire communication cable, with the ground connected at a single point to prevent interference.
To facilitate maintenance, label the newly installed breakers as “power meter Disconnect” so you can easily locate them if the device needs to be power-cycled or turned off.
Step 4: Configuring non-Elum equipment
Configuring Solar Inverters
Some solar inverters may require RS485 control features to be activated. To configure a specific inverter, please refer to the manufacturer’s instructions.
The ePowerControl must communicate with solar inverters to collect data for monitoring purposes. To achieve this, the controller interacts with the inverters to:
- Collect active power output measurements
- Communicate maximum power output setpoints
- Retrieve additional measurement data useful for monitoring operations
Table 3 lists all the accessed variables.
Table 3: Solar inverter variable accessed
| Elum Name | Description | Max Access |
| W | Total active power | Read Only |
| WphA | Active power phase A | Read Only |
| WphB | Active power phase B | Read Only |
| WphC | Active power phase C | Read Only |
| VAR | Total reactive power | Read Only |
| VARphA | Reactive power phase A | Read Only |
| VARphB | Reactive power phase B | Read Only |
| VARphC | Reactive power phase C | Read Only |
| VA | Total apparent power | Read Only |
| VAphA | Apparent power phase A | Read Only |
| VAphB | Apparent power phase B | Read Only |
| VAphC | Apparent power phase C | Read Only |
| Hz | Frequency | Read Only |
| AphA | Current phase A | Read Only |
| AphB | Current phase B | Read Only |
| AphC | Current phase C | Read Only |
| PhVphA | Line voltage phase A | Read Only |
| PhVphB | Line voltage phase B | Read Only |
| PhVphC | Line voltage phase C | Read Only |
| Status | Solar inverter status | Read Only |
| Operating Mode | Solar inverter operating modes | Read Only |
| Alarm | Solar inverter alarms | Read Only |
| WSet | Solar inverter maximum active power setpoint | Read / Write |
Table 4: Requirement for solar inverter
| RS1 | Each inverter must allow Modbus RTU or TCP communication |
| RS2 | Each inverter must allow active power setpoint communication via Modbus RTU or TCP |
Configuring Genset Controllers
To enable remote communication or activate reverse power protection on a genset controller, follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
The ePowerControl must communicate with the genset or its controller to ensure safe operation and collect monitoring data. To perform this task, the controller gathers:
- Active power output measurements
- Additional accessible data needed for site monitoring
Table 5 list all the accessed variables.
Table 5: Genset or genset controller variable accessed
| Elum Name | Description | Max Access |
| W | Total active power | Read Only |
| WphA | Active power phase A | Read Only |
| WphB | Active power phase B | Read Only |
| WphC | Active power phase C | Read Only |
| VAR | Total reactive power | Read Only |
| VARphA | Reactive power phase A | Read Only |
| VARphB | Reactive power phase B | Read Only |
| VARphC | Reactive power phase C | Read Only |
| VA | Total apparent power | Read Only |
| VAphA | Apparent power phase A | Read Only |
| VAphB | Apparent power phase B | Read Only |
| VAphC | Apparent power phase C | Read Only |
| Hz | Frequency | Read Only |
| AphA | Current phase A | Read Only |
| AphB | Current phase B | Read Only |
| AphC | Current phase C | Read Only |
| PhVphA | Line voltage phase A | Read Only |
| PhVphB | Line voltage phase B | Read Only |
| PhVphC | Line voltage phase C | Read Only |
| Status | Genset status | Read Only |
| Operating Mode | Genset operating modes | Read Only |
| Alarm | Genset alarms | Read Only |
| WSet | Gensets active power setpoint | Read / Write |
Table 6: Requirement for genset or genset controller
| RS1 | The genset or the controller must allow Modbus RTU or TCP communication |
Configuring Grid and Load Sensors
The ePowerControl requires data from the Point of Connection (POC) between the site and the external power grid, as well as from the load. This information is gathered through sensors capable of measuring the necessary electrical parameters.
The ePowerControl communicates with the installed power meters to collect:
- Active power measurements
- Relevant data for system monitoring
The power meters provided by Elum are pre-configured to meet these requirements and are used by default.
To set up remote communication on a third-party power meter, refer to:
- The manufacturer’s instructions
- The Device Connection & Configuration Specific Instructions provided by Elum
Table 7: Grid sensor variable accessed
| Elum Name | Description | Max Access |
| W | Total active power | Read Only |
| WphA | Active power phase A | Read Only |
| WphB | Active power phase B | Read Only |
| WphC | Active power phase C | Read Only |
| VAR | Total reactive power | Read Only |
| VARphA | Reactive power phase A | Read Only |
| VARphB | Reactive power phase B | Read Only |
| VARphC | Reactive power phase C | Read Only |
| VA | Total apparent power | Read Only |
| VAphA | Apparent power phase A | Read Only |
| VAphB | Apparent power phase B | Read Only |
| VAphC | Apparent power phase C | Read Only |
| Hz | Frequency | Read Only |
| AphA | Current phase A | Read Only |
| AphB | Current phase B | Read Only |
| AphC | Current phase C | Read Only |
| PhVphA | Line voltage phase A | Read Only |
| PhVphB | Line voltage phase B | Read Only |
| PhVphC | Line voltage phase C | Read Only |
Table 8: Requirement for grid sensor
| RS1 | The sensor must allow Modbus RTU or TCP communication |
Step 5: Installing the ePowerControl
Installation
ℹ️️ Installation location
The ePowerControl is designed for indoor installations. If an outdoor installation is required, a special housing must be specified when placing the order.
ℹ️️ Internet access
A stable internet connection is required for the autonomous deployment of the ePowerControl and for maintenance interventions by Elum engineers. The enclosure should be installed in a location with at least edge-level reception if using a wireless connection, or with a stable local network connection if using a wired connection.
Instructions for ePowerControl delivered in a pre-installed casing
To wall mount the ePowerControl enclosure, follow these steps:
- Remove the mounting plate by unscrewing the four nuts securing it inside the enclosure.
- Mount the Base Station to the wall using the appropriate screws and wall plugs.
- Reattach the mounting plate inside the enclosure.
Instructions for ePowerControl delivered as a kit
If delivered as a kit, all ePowerControl components must be installed on a DIN rail. To prevent the Central Computing Unit from overheating, ensure a 15 cm cooling space on each side of the unit.
Power Supply
To power the electrical enclosure, use the screw terminal block. The allowed voltage range is 100 to 240V AC, with a maximum current draw of 1.30A.
ℹ️️ Power source
The power source supplying the controller must be taken from the load side to ensure it remains powered in both “On-grid” (Grid-connected mode) and “Off-grid” (Genset-connected mode)” operations.
If a UPS is used, its power source must also follow this same rule to guarantee continuous operation of the controller under all conditions.
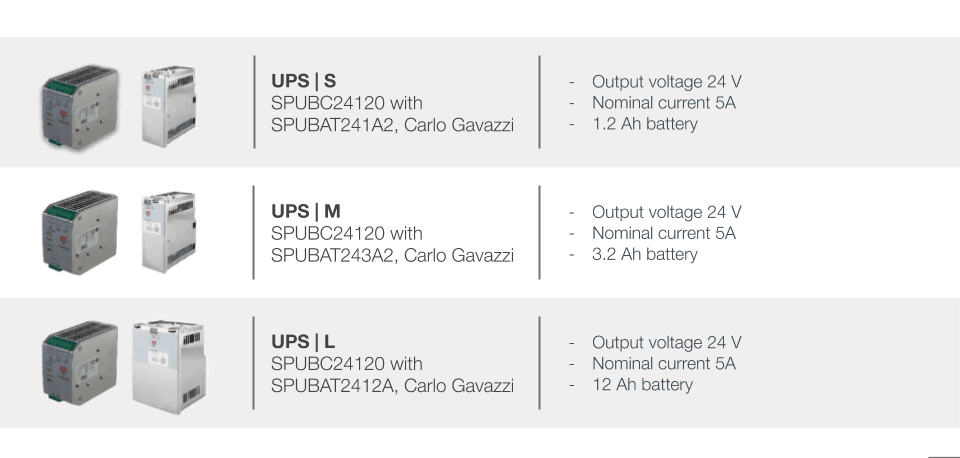
ℹ️️ UPS
For ePowerControl SD, HFS and MC, the use of an UPS is mandatory.
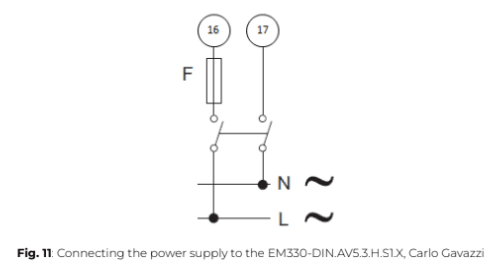
Instructions for connecting the power supply to ePowerControl when in Elum casing
1. The power connectors are pre-wired to a single screw terminal block on the left side of the DIN rail.
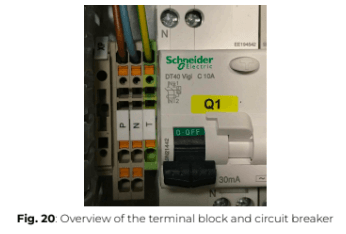
2. Connect the phase wire to the red/brown wire.
3. Connect the neutral wire to the blue wire.
4. Connect the ground wire to the green/yellow wire.
5. If a UPS is included with the ePowerControl, connect the battery red/black wire to the transformer.
6. Engage the circuit breaker to supply power.
7. Verify that the Power LED on the Central Computing Unit is on, confirming proper power connection.
Instructions for connecting the power supply to ePowerControl when in kit
Table 9: ePowerControl Power Supply Parameters
| Input voltage | 12 to 24 VDC |
| Input Current | 480 mA @ 12 VDC 225 mA @24 VDC |
| Power Consumption | 5,4 W |
1. To power the Central Computing Unit (CCU), connect the “terminal block to power jack converter” (included in the package) to the DC terminal block located on the top panel of the unit. Then, connect the power adapter. The system will take approximately 30 seconds to boot up.
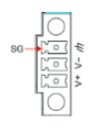
2. Proper grounding and wire routing help reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure stable operation. The shielded ground contact (also known as protected ground) is the top contact of the 3-pin power terminal block connector. Connect the shielded ground wire to a properly grounded metal surface to enhance protection and minimize interference.
ℹ️️ When the ePowerControl is turned on, all LEDs will illuminate for 1 second, then turn off for 60 seconds while the Internet connection and system services initialize.
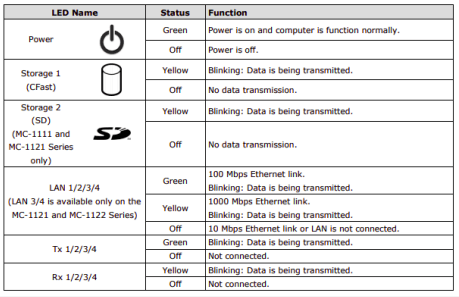
The central processing unit within the ePowerControl controller is equipped with multiple LED indicators that offer a quick overview of the system’s status. Their meanings are detailed in the table below.
Step 6: Setting up ePowerControl in eConf
Before proceeding to the commissioning
Required Materials
To configure internet access, you will need:
- A computer with an Ethernet port
- An Ethernet cable
- If your computer does not have a LAN port, use a USB-to-Ethernet or Type-C-to-Ethernet adapter.
Prerequisite
Before commissioning your system, Elum may require a firmware update to ensure access to the latest version of eConf with the most recent communication drivers. Keeping the drivers updated is essential for reliable communication tests and for conducting wiring reviews and ePowerControl configuration autonomously.
Accessing eConf
2. To access the eConf interface, connect your laptop to LAN 2 of the Central Computing Unit (CCU).
Ensure that the CCU is powered on (check the Power LED).
3. Then, open a web browser and enter 192.168.4.127 in the URL bar to access the configuration settings.
ℹ️️ To access eConf local web page, ensure that your computer’s Ethernet port is configured in DHCP mode.
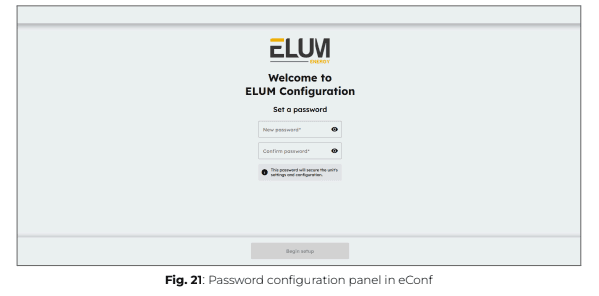
Configuring your password
On the login page, set an access password, which will be required each time you connect to the ePowerControl and access the configuration platform “eConf”. Once the password is set, click “Begin Setup” to proceed.
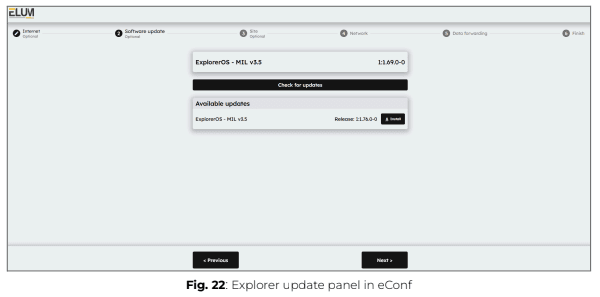
Checking and installing Software Updates
After setting up the password, the system will automatically check for available software updates and display them. However, you can also manually check for updates by clicking on “Check for updates”.
If an update is available, it will appear in the “Available updates” section. To proceed with the update, click the “Install” button. The update process will then begin, ensuring your system runs the most recent version of ExplorerOS.
It is recommended to install the latest available update to ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
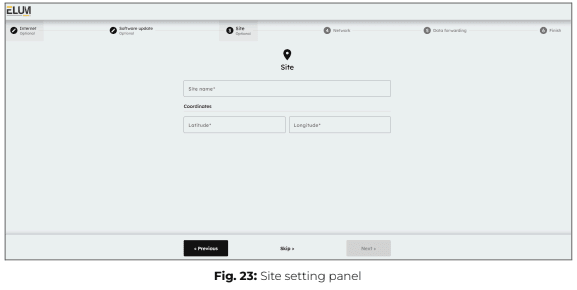
Configuring site settings (optional)
Enter the name and GPS coordinates of the site associated with the ePowercontrol controller.
ℹ️️ The information provided in this panel will be used to configure the ePowerMonitor dashboard. Access to ePowerMonitor requires a subscription to the platform.
Configuring internet access (optional)
After setting up the site settings, you will need to configure the network settings for internet access and device communication.
Configuring a wired internet connection
ℹ️️ The LAN connection that allows the ePowerControl to access the internet via a wired connection must always be made through LAN port 4 of the Central Computing Unit (CCU). If additional LAN ports are needed, a network switch can be connected to LAN port 1, 2 or 3.
ℹ️️ To properly configure the internet connection, coordination with the IT team is essential. The following outgoing IPv4 network accesses must be allowed for the controller to communicate with the Elum backend servers:
● ICMP (Ping Protocol)
● TCP Ports: 53, 80, 443, 4505, 4506
● UDP Ports: 53, 123, 1195
Additionally, before installation, request the network configuration details that should be applied to the ePowerControl to ensure proper connectivity.
No optional module is required to establish a wired internet connection between the ePowerControl and the internet.
1. Click on “+ Configure a new connection” and select “Internet access”, then choose “Wired Access – LAN1”.
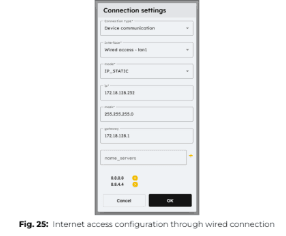
2. Enter the appropriate connection parameters based on your network settings and press OK.
3. Click the “Test” button to verify the connection. 
Configuring a cellular internet connection
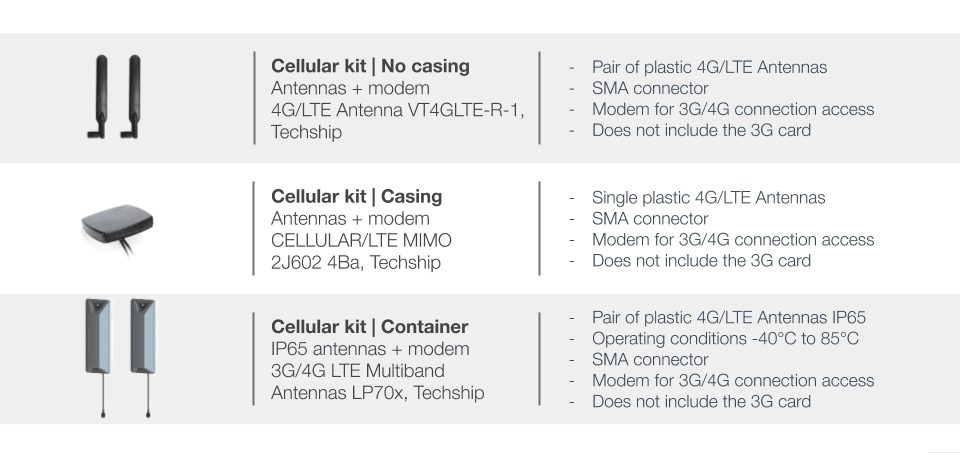
ℹ️️ The GSM/3G module is pre-installed in the Central Computing Unit (CCU). However, you will need a SIM card with a valid data subscription to enable connectivity.
⚠️ The ePowerControl must be turned off before inserting or removing the SIM card.
If you need to change the SIM card, an empty start (powering on without a SIM card before inserting the new one) must be performed.
For these steps, the Central Computing Unit must NOT be powered on.
1. Connect the two wireless antennas to the dedicated connectors on the front
panel of the CCU.
2. Insert the SIM card into the SIM card slot.
ℹ️️ To access the SIM card slot, use a screwdriver to open the cover.
Insert the SIM card directly into the slot until you hear a “click”, indicating it is securely in place.
3. Power ON the Central Computing Unit (CCU).
ℹ️️ Upon startup, all LEDs will turn ON for 1 second, then turn OFF for 60 seconds while the system initializes.
4. Wait approximately 1 minute for the startup process to complete.
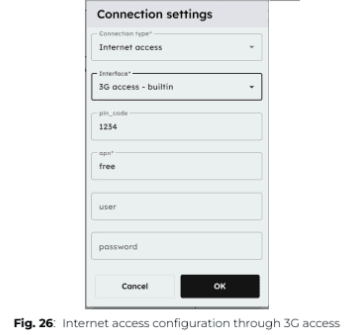
5. In the Network Configuration Panel, click “+ Configure a new connection” and select “Internet access”, then choose “3G Access – Built-in”.
6. Enter the appropriate connection parameters for your network and press OK.
7. Test the connection by clicking the “Test” button. 
ℹ️️ To obtain your SIM card PIN number, APN address, and required credentials, please refer to the documentation provided by your service provider. These details are necessary to configure the GSM/3G connection on the ePowerControl.
Configuring ports and devices
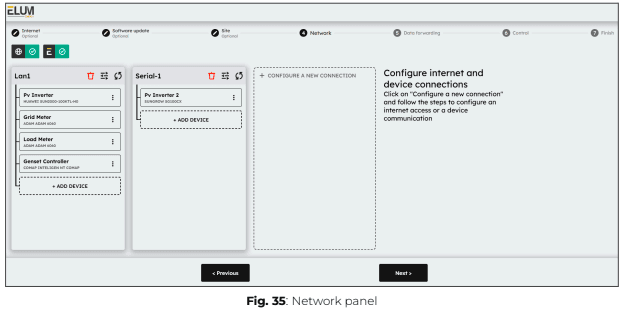
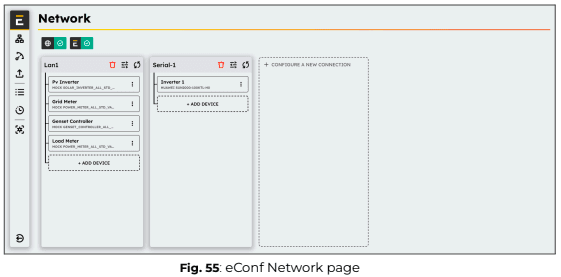
Once the wiring and internet configuration is complete, you can proceed with setting up communication between the ePowerControl and connected devices.
From eConf you have to configure each connection corresponding to each of the ports of the Central Computing Unit which are used.
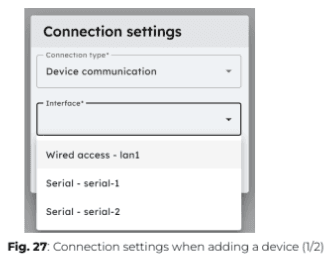
1. Click “+ Configure a new connection” and select “Device communication”, then choose the appropriate interface.
ℹ️️ Only unused interfaces will be available in the drop-down list. If a port has already been configured, you can edit its settings directly. 
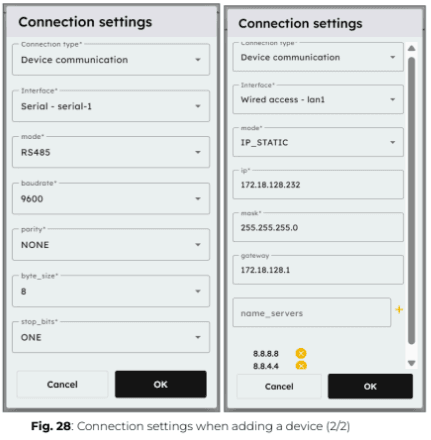
2. Apply the correct connection settings based on the device requirements.
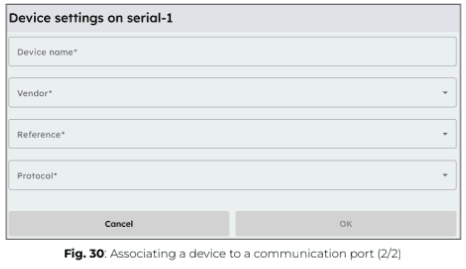
3. Once the connection is configured, add each device one by one by clicking “+ Add device”.
4. Apply the correct parameters for each device to ensure proper communication.
ℹ️️ Communication parameters
Modbus RTU:
- Slave ID: Unique identifier for the device.
- Response Timeout (default: 0.5s): Maximum waiting time before receiving the first byte of the response.
- Byte Timeout (default: 0.1s) : Maximum waiting time between subsequent bytes in the response.
Modbus TCP:
- IP Address: The device’s network address.
- Port (default: 502): The communication port used for Modbus TCP.
- Slave ID: Unique identifier for the device.
- Response Timeout (default: 0.5s): Maximum waiting time before receiving the first byte of the response.
- Byte Timeout (default: 0.1s): Maximum waiting time between subsequent bytes in the response
SNMP:
- IP Address: The device’s network address. Community: The SNMP community string for authentication.
- Port (default: 161): The communication port for SNMP.
- Transport (default: UDP): The protocol used for SNMP communication.
- Timeout (default: 0.5s): Maximum waiting time before receiving a response.
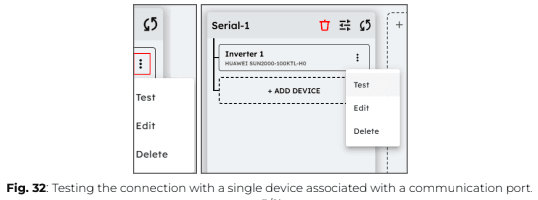
5. To test all devices linked to a specific connection port on the Central Computing Unit (CCU), click on “Test” in the connection settings. 
To test a single device independently, click on the three dots next to the device name, then select “Test”.
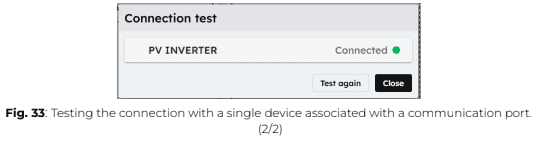
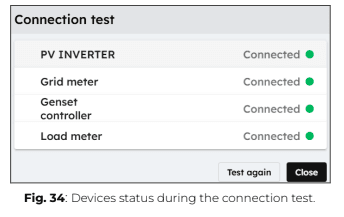
When you run a connection test from the eConf interface, the ePowerControl sends a read request to the connected equipment.
● If the test is successful, the device status will be displayed as “Connected”.
● If the test fails, the device status will be shown as “Disconnected”.
ℹ️️ Driver error
If the test returns a “Driver error”, it means the device is “Connected”, but the driver needs to be updated remotely by Elum. In this case, please notify the Elum Deployment Team for assistance.
6. Once all ports and devices have been correctly configured and all connection tests have been successful, click “Continue” to proceed.
⚠️ It is essential to only start data acquisition once functional communication has been established with all necessary and useful equipment on-site. If any equipment is still marked as “Disconnected” in eConf after commissioning, Elum cannot be held responsible for any malfunction of the monitoring and control system.
Configuring data forwarding (optional)
Elum offers an optional data export feature, allowing data to be forwarded to third-party platforms or USB devices. If you do not need to export data to any platform other than ePowerMonitor or to a USB device, click “Skip” to move to the next configuration section.
Available Data Export options:
- FTP Push to Energysoft: Exports data to the Energysoft monitoring platform using the S4E PowerAPI data format.
- FTP Push to Other Servers: Sends data to any internal or external server supporting the FTP protocol, using the Elum Energy data format.
- Meteocontrol Export: Enables data export to the Meteocontrol platform. The serial number of the controller must be registered on the Meteocontrol interface for data export to be enabled. Users can configure:
- USB Export: Saves data directly to a USB device for local storage.
ℹ️️ For more details about the Elum Data Export feature and supported data formats, contact Elum support at support@elum-energy.com.
ℹ️️ If needed, all export methods can be activated simultaneously.
Start by selecting an export method from the available options. Once chosen, you will be prompted to enter additional details required to configure the data forwarding settings.
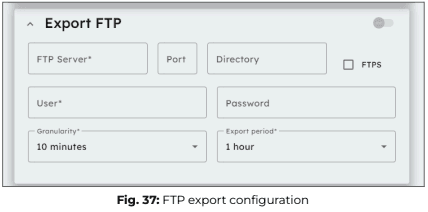
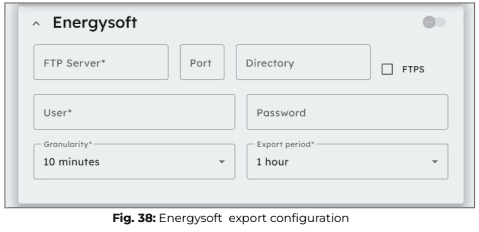
Export FTP
- Enter the FTP server details, including the server address, port, and directory, where you want to forward your data.
- Provide your user credentials (Username and Password) to authenticate access to the specified FTP server.
- Set the data granularity, which determines how frequently data points are recorded before being forwarded. This can range from 5 minutes to 1 day.
- Specify the export period, which defines how often the collected data is sent to the FTP server. This setting is independent of granularity and can range from 10 minutes to 1 day.
- Enable FTPS (via the checkbox) if you require a secure connection using FTP over SSL/TLS to enhance data encryption and security during transmission.
Energysoft
The Energysoft export method operates using the FTP protocol, similar to Elum’s standard FTP push service, with the only difference being the export file format. Therefore, the same FTP forwarding settings apply to both methods.
For further information see previous section Export FTP.
Meteocontrol Export
The Meteocontrol export option enables the ePowerControl to forward data to the Meteocontrol platform for monitoring and analysis. To activate this feature, the serial number displayed on the (eConf must be registered on the Meteocontrol interface).
Configuration parameters:
- Serial number: The unique identifier generated by eConf, which must be registered in the Meteocontrol platform to activate data export.
- Granularity: Defines how often data is collected before being forwarded. This can be set between 5 minutes and 1 hour.
- Export period: Determines how often the collected data is sent to Meteocontrol, with options ranging from 10 minutes to 1 day.
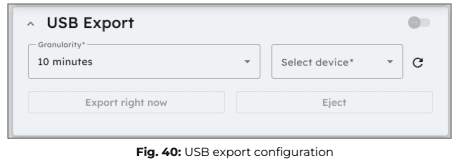
USB Export
When a USB device is plugged into the Elum Explorer USB port, it will appear in the device selection list within the USB export configuration panel. Select the USB device where you want to forward your data.
Configuration parameters:
- Granularity: Defines how often data is collected before being saved to the USB device.
- Export Period: The export period is fixed at 24 hours, with all data being exported once per day at 00:00 UTC.
Manual data export & Ejecting USB device
- By clicking “Export right now”, the data from the current export period will be immediately saved to the USB device.
- It is highly recommended to use “Export right now” just before ejecting your USB device to ensure all collected data is saved.
- To safely remove your USB device, click “Eject” before physically unplugging it.
- Failure to eject the USB device properly may result in data loss or permanent damage to the USB storage.
ℹ️️ To prevent damage to your USB device and avoid irreversible data loss, always eject the USB device before physically removing it from the Elum Explorer USB port.
Control panel overview
The Control panel in eConf allows you to configure and input power-related data for the different components of your power system. It is where you set up the grid meters, genset meters, and I/O modules, ensuring proper monitoring and control of the installation.
Depending on the model of ePowerControl and the application type (PV + Grid, PV + Genset, or PV + Genset + Grid), different sub-tabs may be displayed for configuration.
Available control sub-tabs
- PV control: Configure the photovoltaic system settings, including power limitations and inverter parameters.
- Genset control: Set up genset parameters, including startup thresholds and control strategies.
- Grid control: Configure grid interaction settings, including grid meters and connection rules.
- Load breaker control: Manage the load breaker settings for system protection or transition.
- Production breaker control: Configure production breaker settings to ensure safe power dispatching.
Main configuration sections
- Grid meters: Set up power meters that measure the grid’s power flow at the point of common coupling.
- Genset meters: Configure genset power meters and define the unit detection method (e.g., frequency-based).
- Multi-purpose I/O modules: Configure I/O modules that allow communication with grid breakers and load breakers.
This Control panel is essential for defining power control strategies and ensuring seamless communication between system components.
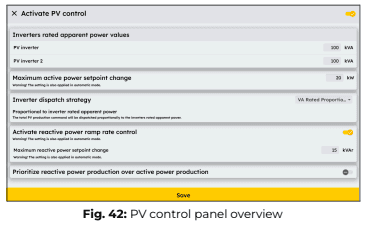
PV Control configuration
The PV Control tab in eConf allows you to activate or deactivate PV control and configure how the EMS computes and dispatches power setpoints to the inverters. When activated, the EMS determines both active and reactive power setpoints according to system requirements and control strategies.
In this tab, you can:
- Define the maximum apparent power (kVA) of the connected inverters, ensuring the system adheres to configured power limits.
- Configure active and reactive power ramp rates, ensuring smooth power variation.
- Select a dispatch strategy for optimal inverter power distribution.
a) Maximum active power setpoint change
This setting controls the ramp rate for how quickly the PV inverters adjust their power output. It ensures gradual changes, preventing sudden power fluctuations that could impact grid stability.
b) PV Dispatch strategies
To optimize PV performance, the EMS offers two dispatch strategies:
- VA Rated Proportional Dispatch: The PV plant’s total power is distributed based on each inverter’s nominal power.
- Optimized Dispatch: Power commands are based on actual inverter output, ensuring more accurate and dynamic power adjustments.
c) Activate reactive power ramp rate control
- This setting determines whether reactive power setpoints should change gradually or instantly.
- By default, it is disabled (False).
- When activated (True), it enables the maximum reactive power setpoint change field, allowing you to set a maximum allowable change rate for reactive power adjustments.
d) Prioritize reactive power production over active power production
This setting determines whether the PV system prioritizes reactive power before active power.
- When activated (True):
○ The system will first fulfill reactive power requirements.
○ Active power output may be reduced depending on remaining capacity. - When deactivated (False : Default):
○ The system prioritizes active power production.
○ Reactive power is adjusted only after fulfilling active power needs.
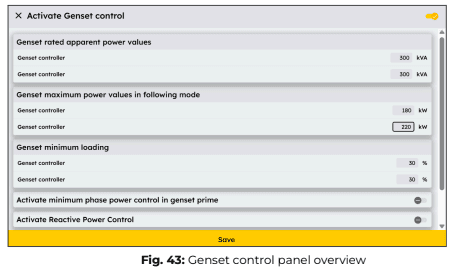
Genset Control configuration
The Genset Control tab in eConf allows you to activate or deactivate genset control and configure the operational settings for connected gensets. The ePowerControl can automatically manage genset operation based on the selected mode:
- Following mode (Direct Control): The EMS sends setpoints directly to the genset controller via Modbus.
- Forming mode (Indirect Control): The EMS does not directly control the genset but instead monitors its power output and adjusts PV system setpoints to influence genset production.
In this tab, you can define genset power parameters, set power limits, activate reactive power control, and configure automatic genset start/stop functions.
a) Rated Apparent Power
- Define the rated apparent power (kVA) of each genset.
- The maximum power value in following mode must always be less than or equal to the rated apparent power.
b) Genset minimum loading
- Ensures that the genset does not operate below a defined minimum power level.
- If necessary, the EMS will curtail PV production to maintain this threshold.
- For multiple gensets:
○ If the total setpoint is below the sum of minimum loadings, power is distributed proportionally to ensure each genset meets itsminimum threshold.
○ If the total setpoint exceeds the sum of minimum loadings, poweris first allocated to ensure all gensets reach their minimum before distributing remaining power. - In forming mode, the EMS adjusts other controllable devices to maintain gensets above their minimum loading percentage.
c) Activate minimum phase power control in genset prime
This function ensures that in Genset Prime mode, the PV system adjusts its output to keep the lowest phase’s active power above a defined threshold.
- If the power in any genset phase falls below the set minimum, the EMS will adjust the PV inverters or other controllable devices to boost the genset’s power output.
- This helps maintain balance across all three phases, preventing uneven load distribution that could cause instability.
- Ideally, the active power should be evenly distributed among the three phases of a genset system.
d) Activate reactive power control
The Genset reactive power control function ensures a stable and efficient power factor by coordinating the production of reactive power between PV inverters and gensets.
- If the genset alone cannot maintain the desired power factor, the PV inverters provide additional reactive power support.
- Reactive power calculation:
○ The EMS continuously monitors the genset’s power factor and the reactive power produced by the genset. - Reactive power setpoint dispatch:
○ The EMS calculates the necessary reactive power to meet the target power factor.
○ The calculated value is sent to PV inverters, which adjust their reactive power output accordingly. - Maintaining the genset power factor: The EMS balances reactive power by adjusting PV inverter output when needed:
○ Defined Range: Ensures that the genset’s power factor remains within a pre-defined range (either inductive or capacitive).
○ Fixed Target: The EMS maintains a specific power factor value by adjusting reactive power dynamically.
e) Automatic genset Start/stop
This function automates genset activation and deactivation in a grid-connected system for peak shaving and import limit control.
Key Parameters:
- Margin before target:
○ Defines a power margin to trigger peak shaving before reaching the limit.
○ Ensures that gensets activate early to avoid exceeding import limits. - Start delay:
○ Sets a time delay before starting gensets. - Prevents gensets from activating due to temporary power surges.
- Stop delay:
○ Sets a time delay before stopping gensets.
○ Ensures gensets are not turned off too quickly due to short-term power drops.
f) Genset Commitment Strategy
When multiple gensets are available, this function determines how many gensets should start based on real-time power demand. The three available strategies are:
- Start All: Activates all configured gensets simultaneously to meet power demand.
- Start One: Starts only the genset with the least total engine runtime.
- Adaptive: Dynamically adjusts the number of active gensets based on power demand.
Grid Control configuration
The Grid Control Panel allows you to configure power exchange settings between the site and the local grid. It ensures compliance with grid regulations, optimizes energy flows, and provides control over both active and reactive power. Below are the key functionalities available in this section:
a) Activate active power export control
The Export Control function manages how much active power the PV inverters can send to the grid, ensuring that power levels at the Point of Common Coupling (PCC) stay within defined limits. This prevents the site from exceeding the permitted export threshold.
- Minimum active power at PCC
○ Positive value: The EMS ensures the site imports at least the defined power from the grid (no export allowed).
○ Negative value: The EMS allows exporting power up to the specified limit while still allowing grid imports.
This feature ensures grid stability by managing power flow between the site and the grid, and it is applicable in Grid Prime Configuration.
- Sensing method for the Grid Meter
Determines how the system calculates active power reference for export control. Two methods are available:
- Sum of all phases: Uses the total active power from all three phases combined.
- 3x Lowest Phase: Dynamically identifies the lowest phase power and multiplies it by three. This helps maintain phase balance in asymmetrical grid conditions.
b) Peak Shaving
Peak shaving prevents the grid from importing excessive power due to load surges or drops in PV production. It achieves this by automatically adjusting genset production or PV curtailment.
- Activate peak shaving with genset
- Enables automatic genset production adjustment to limit grid import.
- Requires activation of automatic genset start/stop in Genset Control settings.
- Peak shaving target
- Defines the maximum active power import limit at different times of the day.
- Configurable via a daily schedule with up to two-day categories and ten time slots per category.
- Sensing method for the grid meter: Determines how the system calculates the active power reference for peak shaving:
- Sum of all phases: Uses the total active power from all three phases combined.
- 3x Highest Phase: Uses three times the highest phase power, ensuring phase balance in asymmetrical conditions.
c) Activate reactive power control
This feature automatically adjusts reactive power to keep the grid power factor within a defined range or at a target value. It does this by sending reactive power setpoints to the PV inverters.
- Controlled units: The system identifies which units (e.g., PV inverters) will be responsible for reactive power regulation.
- Maximum absolute value of reactive power petpoint for PV: Defines the upper limit for how much reactive power PV inverters can absorb or inject into the grid
- Reactive power control strategies: Two strategies are available:
- Power factor range maintains the power factor within a predefined range by setting:
- Minimum capacitive power factor: Defines the lowest allowable
leading (capacitive) power factor. - Minimum inductive power factor: Defines the lowest allowable
lagging (inductive) power factor.
- Minimum capacitive power factor: Defines the lowest allowable
- Power Factor Target: Keeps the power factor at PCC fixed to a specific value.
- Power factor range maintains the power factor within a predefined range by setting:
Grid Meters
This tab enables you to define and configure grid meters that provide power measurements at the Point of Common Coupling (PCC). These meters must first be added and configured in the Network tab of eConf before being assigned here.
Genset Meters
This tab allows you to configure genset meters, which measure power when running on genset power. These meters also determine the operational status (ON/OFF) of the genset.
- Genset ON/OFF Detection Methods
The EMS can determine if a genset is running using two different detection methods:- Frequency-based detection : If the measured frequency exceeds the configured threshold, the genset is considered ON.
- Power-based detection : If the measured power (as a percentage of the rated genset power) exceeds a defined limit, the genset is considered ON. The rated power is configured in the Genset Control tab.
Multi-Purpose IO Modules
This tab enables you to configure how breakers are controlled using multi-purpose IO modules (MPIOs). The setup is done in the Network tab of eConf.
Each MPIO module can control up to three breakers, with a total of five MPIO units available, allowing for control of up to 15 breakers.
- Types of breakers
- Production Breaker : Controls power production sources.
- Load Breaker: Controls power consumption loads.
- Breaker control types: The EMS can open or close breakers based on specific conditions:
- Load power (Grid Prime/ Genset Prime): Opens/closes a breaker based on load levels.
- Grid import (Grid Prime): Controls breakers based on grid import limits.
- Genset loading (Genset Prime): Ensures proper genset loading by controlling breaker status.
Starting the EMS
1. Confirm that you want to complete the setup by clicking on “Finish Setup”.
The data entered during the setup process can be modified later through the eConf configuration platform.
2. Once you click on the “Finish Setup” button, you will be redirected to the Overview page of the eConf configuration platform.
ℹ️️ Load meter
The load power meter can be useful for the installer to perform consistency checks, but it is not a mandatory component for the proper functioning of the ePowerControl.
If no load meter is installed, the Load Meter field can be left blank.
However, if a load indicator is detected by the control panel, it will be integrated into the EMS control loop as a critical device and will be considered when triggering the safety mode.
Step 7: Functional tests
Test environment configuration
To perform the functional tests, ensure that your computer remains connected to the controller and that you are logged into eConf interface..
EMS status
Before proceeding with the functional tests, ensure that:
- Data acquisition has already been launched.
- The EMS control status is displayed as “ON”, indicating that the EMS is actively computing and dispatching production.
PV injection
During the entire deployment process, PV injection must remain shut down. This requirement also applies to the functional tests configuration, meaning PV injection should stay off initially.
Devices connection status
By this stage of commissioning, all equipment to be monitored and controlled by the Elum controller should be properly connected. You can verify the connection status of each device through eConf Devices panel.
Consistency check up
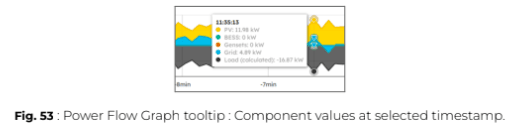
In the Overview and Devices panels of eConf, real-time data is displayed and automatically refreshed. You must perform a consistency check, particularly to validate the correct configuration of power meters.
ℹ️️ Power meters consistency check
Proper power meter installation depends on the correct positioning and wiring of Current Transformers (CTs) and Voltage Transformers (VTs). Ensure the following:
- CTs and VTs must be installed on the correct bus bar/wires, matching the exact measurement point of interest.
- CTs must be installed in the correct direction to ensure accurate readings.
- Grid power consumption should always be displayed as a positive value.
- Load power consumption should always be displayed as a positive value.
- Genset(s) power production should always be displayed as a positive value.
- CTs and VTs must correspond phase by phase, a phase swap will affect the power factor (cos φ) measurement, leading to incorrect readings.
Test procedures
The test procedures vary depending on the EMS application being used. Please follow the specific instructions for the EMS application selected in eConf Control panel.
Each step of the procedure must be strictly followed according to the instructions provided in this section.
If, at any point during the test procedure, the outcome differs from the expected result described, contact the Elum Deployment Team at support@elum-energy.com for assistance.
On-Grid (PV + Grid application) & Islanded (PV + Genset)
Follow the steps below carefully. Proceed to the next step only when your test results match the expected outcome described in this user manual.
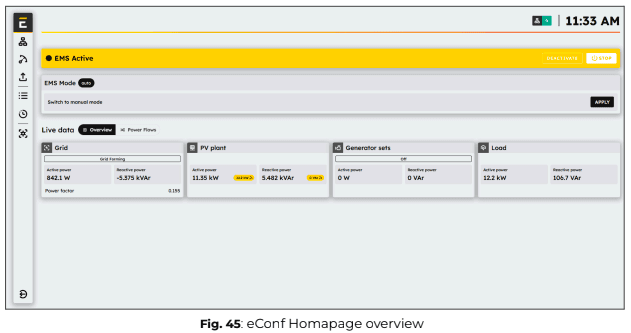
1. Go to the Overview page in eConf.
Normally, the EMS should be running, and its status should be displayed as “EMS ACTIVE”.
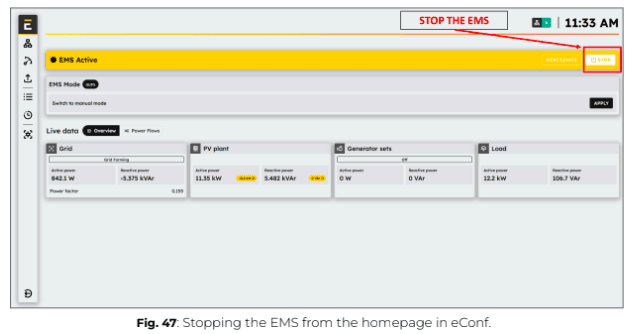
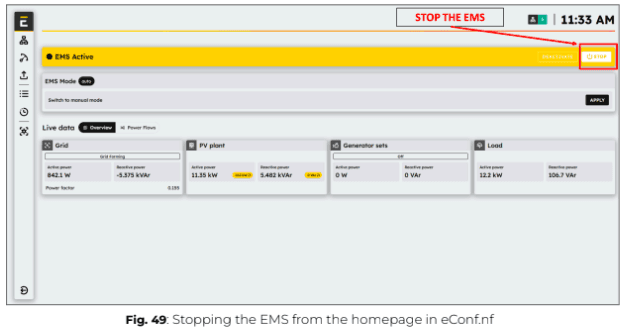
2. Click on “Stop” to shut down the EMS from the Overview page in eConf.
Expected outcome: The EMS control status should first display “EMS FORCE STOPPING”, and then change to “EMS OFF”, confirming that the EMS has been successfully shut down.
ℹ️️ When the EMS is stopped:
- All control features of the EMS are disabled.
- PV inverters are curtailed to their minimum AC power output level.
- Datalogging functions remain active, allowing continuous data collection.
3. Step 1: Turn on PV injection for one of the inverters.
Expected outcome: The AC power output of the inverter must remain below 1% of itsnominal output power.
4. Step 2: If you have multiple PV inverter brands and models, turn off all inverters and restart this step for each brand and reference individually.
Expected outcome: For each brand and model, the AC power output must remain below 1% of the nominal power.
5. Step 3: Turn on all PV inverters simultaneously.
Expected outcome: The AC power output of each inverter must still remain below 1% of its nominal output power.
6. Step 4: Start the EMS and activate PV injection by clicking on the appropriate control button in eConf.
- Expected outcome 1: The EMS control status should first display “EMS STARTING” for a few seconds, then switch to “EMS ON”, indicating that the Energy Management System is fully operational.
- Expected outcome 2: PV injection should begin slowly, increasing power
output gradually.
Backup (PV + Genset + Grid)
Please find below the testing procedure, you must only move from one step to the following when your test results have been those described in this User Manual
1. Ensure that the EMS is ON, and both grid control and genset control are activated and correctly configured with the necessary parameters.
2. Manually simulate a grid failure by opening the grid breaker.
- ePowerControl must remain powered during the transition from “On grid, Grid connected” to “Off grid, Genset connected” configuration.
- This outcome also serves as a valid test for verifying UPS functionality.
Additional Consideration:
- Since Elum controllers are always provided with a UPS, this test helps confirm its operation.
- If you do not connect UPS, this step is critical for ensuring that the system remains powered during grid failure.
ℹ️️ You can verify if the ePowerControl is turned on by checking the Power LED on the front panel of the Central Computing Unit.

Expected outcome 1: Grid, Load, and Genset power meters must remain powered after the gensets have started.
Expected Outcome 2: Genset power meter readings must be consistent with the Load power meter readings (i.e., their values should be equal).
Expected Outcome 3: Grid power meter readings must be consistent and show null values, confirming that the site is no longer drawing power from the grid.
1. Go to the Overview page in eConf.
Normally, the EMS should be running, and its status should be displayed as “EMS ACTIVE”.
1. Click on “Stop” to shut down the EMS from the Overview page in eConf.

Expected outcome: The EMS control status should first display “EMS FORCE STOPPING”, and then change to “EMS OFF”, confirming that the EMS has been successfully shut down.
ℹ️️ When the EMS is stopped, its control features are disabled, and the PV inverters are limited to their minimum AC power output, while datalogging remains active.
2. Start PV injection of one of the inverters.
Expected outcome: The AC power output of the inverter must remain below 1% of the PV inverter nominal output power.
3. If you have different brands and references of PV inverters, turn off all the inverters again and start over at this step 3 until you have tested independently all of the PV inverters brands and references.
Expected outcome: The AC power output of the inverter must remain below 1% of the PV inverter nominal output power, for each brand and reference of PV inverter.
4. Turn on all the PV inverters one by one.
Expected outcome: The AC power output of each inverter must remain below 1% of the PV inverter nominal output power.
5. Step 4: Start the EMS and activate PV injection by clicking on the appropriate control button in eConf.
- Expected outcome 1: The EMS control status should first display “EMS STARTING” for a few seconds, then switch to “EMS ON”, indicating that the Energy Management System is fully operational.
Expected outcome 2: PV injection should begin slowly, increasing power output gradually.
6. Manually transition the power plant from “Off grid, Genset connected” to “On grid, Grid connected” by closing the grid breaker.
Expected Outcome 1: ePowerControl must remain powered during the transition from “Off grid, Genset connected” to “On grid, Grid connected” configuration.
Expected Outcome 2: Grid, Load, and Genset power meters must be powered once the system has switched back to “On grid, Grid connected” configuration.
Verification of zero export control and reactive power regulation
If the system is configured with multiple grid injection points, the zero export control must be verified for each point. This ensures that no power is injected into the grid at any monitored location.
a) Zero Export Test for Multi-Point Injection
- Verify the configuration of multiple grid monitoring points in eConf.
- Start the EMS and allow it to regulate power based on zero export settings.
- Check the real-time grid power measurements at each injection point.
Expected Outcome: The site should not inject active power into the grid at any monitored injection point.
- If active power injection is detected at any point, contact Elum Support for assistance.
b) Reactive power control test
The controller can regulate the grid power factor by controlling reactive power. This test ensures that the system correctly adjusts reactive power to maintain the target power factor.
- Configure the desired grid power factor target in the Grid Control tab.
- Start the EMS and allow it to regulate the system.
- Monitor the power factor at the PCC using the grid meter.
Expected Outcome: The measured power factor should stay within the defined range or match the set target.
- If the power factor deviates from the expected value, verify the reactive power settings and contact Elum Support if the issue persists.
c) Genset minimum loading test
This test ensures that the genset never operates below its defined minimum loading threshold, as running under this limit can cause inefficiencies, increased fuel consumption, and potential mechanical wear.
The Genset Minimum Loading function is designed to keep the genset running at a safe and efficient power level, preventing it from operating under an inadequate load.
- Verify the genset minimum loading threshold configured in the Genset Control tab (e.g., 30% of the genset’s nominal power).
- Start the genset and allow it to stabilize.
- Monitor the genset’s active power output in real time.
- Observe its operation under different load conditions:
- If the genset power is below the minimum loading threshold, corrective measures should be applied according to the system configuration.
- If the genset power is at or above the minimum loading threshold, normal operation should continue.
Expected outcomes:
- The genset should never operate below its configured minimum loading value.
- If the load decreases below the threshold, the system should take corrective actions based on the defined configuration.
- The genset maintains stable operation without running underloaded
Test Conclusion
Once all test procedures have been rigorously followed and each step has resulted in the expected outcomes described in this document, the EMS can be considered fully commissioned.
All results and comments should be documented in the Test Matrix for record-keeping.
On-Grid (PV + Grid application) & Islanded (PV + Genset) test matrix
Table 10: Test Conclusion for On-Grid (PV + Grid) & Islanded (PV + Genset) Applications
| Steps | Expected outcome |
| Accessing eConf Overview | Ensure the EMS is running and its status is displayed as “EMS ACTIVE.” |
| Stopping the EMS | Click “Stop” in eConf. EMS control status should first display “EMS FORCE STOPPING” and then change to “EMS OFF,” confirming shutdown. |
| Testing PV Injection for Individual Inverters | Turn on PV injection for one inverter at a time. The inverter’s AC power output must remain below 1% of its nominal output power. |
| Testing Multiple PV Inverter Brands and Models | If different inverter brands or models are used, turn off all inverters and restart the test for each brand separately. The AC power output must remain below 1% of the nominal power. |
| Testing All PV Inverters Together | Turn on all PV inverters simultaneously. The AC power output of each inverter must still remain below 1% of its nominal output power. |
| Starting the EMS and Enabling PV Injection | Click the appropriate control button in eConf to start the EMS and activate PV injection. The EMS control status should first display “EMS STARTING” and then switch to “EMS ON.” PV injection should gradually ramp up, increasing power output smoothly. |
| Expected outcome 2: PV injection should begin slowly, increasing power output gradually. |
Backup (PV + Genset + Grid) test matrix
Table 11: Test Conclusion for Backup (PV + Genset + Grid) Application
| Steps | Expected outcome |
| Ensure that the EMS is ON, and both grid control and genset control are activated and correctly configured. | The system is ready for testing with all required parameters set. |
| Manually simulate a grid failure by opening the grid breaker. | ePowerControl must remain powered during the transition from ‘On grid, Grid connected’ to ‘Off grid, Genset connected’. This also serves as a valid test for verifying UPS functionality. |
| Go to the Overview page in eConf. | EMS should be running, and its status should be displayed as ‘EMS ACTIVE’. |
| Click on ‘Stop’ to shut down the EMS from the Overview page in eConf. | The EMS control status should first display ‘EMS FORCE STOPPING’ and then change to ‘EMS OFF’, confirming that the EMS has been successfully shut down. |
| Start PV injection of one of the inverters. | The AC power output of the inverter must remain below 1% of its nominal output power. |
| If you have multiple PV inverter brands and models, turn off all inverters and restart this step for each brand and reference individually. | For each brand and model, the AC power output must remain below 1% of the nominal power. |
| Turn on all the PV inverters one by one. | The AC power output of each inverter must still remain below 1% of its nominal output power. |
| Start the EMS and activate PV injection by clicking on the appropriate control button in eConf. | EMS control status should first display ‘EMS STARTING’ for a few seconds, then switch to ‘EMS ON’. PV injection should begin slowly, increasing power output gradually. |
| Manually transition the power plant from ‘Off grid, Genset connected’ to ‘On grid, Grid connected’ by closing the grid breaker. | ePowerControl must remain powered during the transition. Grid, Load, and Genset power meters must be powered once the system. |
Zero Export and Reactive Power Test Matrix
Table 12: Test Conclusion for Zero Export and Reactive Power Regulation
| Steps | Expected outcome |
| Verify the configuration of multiple grid monitoring points in eConf. |
|
| Start the EMS and allow it to regulate power based on zero export settings. |
|
| Check the real-time grid power measurements at each injection point. | If active power injection is detected, the user must contact Elum Support. |
| Configure the desired grid power factor target in the Grid Control tab. | The power factor settings should match the intended target values. |
| Start the EMS and allow it to regulate the system. | The EMS should adjust reactive power to maintain the set power factor. |
| Monitor the power factor at the PCC using the grid meter. | The measured power factor should stay within the defined range or match the set target. If deviations occur, verify the reactive power settings or contact Elum Support. |
eConf navigation after the commissioning
Accessing eConf
After deploying the ePowerControl, the eConf interface remains accessible at any time for further adjustments or diagnostics.
To access the interface:
1. Connect your laptop to LAN2 of the Central Computing Unit (CCU).
2. Open a web browser and enter 192.168.4.127 in the URL bar.
User interface: eConf
General information
The main purposes of eConf are:
- To configure the site: Set up network parameters, connected devices, and system settings.
- To define the control rules: Establish operational rules for managing site behavior.
- To monitor the logs: Track system logs, events, setpoints, and errors.
- To monitor the behavior of the site: Observe real-time data and performance of all connected devices
ℹ️️ Forgot password?
If the User password is forgotten, Elum can generate a backup password upon request.
This backup password will be valid for 24 hours and can be used to log in and set a new password from the Password panel in eConf interface.
Supported language
The eConf interface supports the following languages:
- English
- French
The language selection is automatically determined by the browser’s language settings.
In solutions that include a screen, it may not always be possible to change the browser’s language. If this issue occurs, please contact Elum Support for guidance and assistance.
Overview
The Live Data Overview Panel provides a real-time summary of your power plant’s status. It displays essential information on power generation, consumption, and control operations, helping operators monitor system performance at a glance.
Once configuration is complete and the EMS is activated, the system automatically redirects the user to this page.
Main Overview panel
This central section of the interface includes:
- Control Actions: Located at the top-right, operators can:
○ Start, Stop, or Force Stop the EMS.
○ Deactivate automatic control when necessary.
These actions allow manual intervention during critical operations. - Current EMS Mode: Displays whether the EMS is running in Auto or Manual mode. You can switch between modes using the “Switch to manual mode” button and applying changes.
- Current EMS State: Indicates the real-time operational status of the EMS.
- Power Monitoring Summary: Shows active and reactive power metrics for each connected unit:
○ Grid: Power import/export and power factor.
○ PV Plant: Current solar generation values.
○ Generator Sets: On/Off status and output data.
○ Load: Total site consumption (active and reactive power). - Current EMS Setpoints: Highlighted in yellow circles, these indicate active control targets applied by the EMS to maintain optimal system performance.
- Active Components Counter: Displayed in the top-right corner next to the clock, showing the total number of components in the system and their current status.
Power flow view
The Power Flows view provides an intuitive and real-time visualization of energy flows within the power plant. It is designed to help you monitor the dynamic interactions between generation, storage, consumption, and grid exchange.
The Power Flow graph (Timeline graph) shows active power (kW) values for each major component of the power plant over the last 10 minutes:
- Stacked color bands: Each band represents a component:
- PV (yellow)
- Grid (blue)
- Gensets (orange)
- Load (dark gray/black)
- Battery (Green)
- Positive values: Represent energy generation or export.
- Negative values: Represent energy consumption or import.
- Tooltip on hover: Displays the exact active power values of all components at a specific timestamp.
Reactive power is not displayed in the timeline graph but is shown in the component list below the graph:
- For each component (PV, Grid, Gensets, Load), both active and reactive power are displayed in real time.
- Yellow highlighted values: Represent EMS control setpoints applied to the system.
- Status squares (🟩🟧🟥): Indicate the communication and operational status of each component:
- Green (🟩): The device is communicating and functioning properly.
- Orange (🟧): There is an issue with communication to one or more registers of the device.
- Red (🟥): The device is disconnected or not communicating
Left side menu
The vertical menu on the left provides access to all major functionalities of the (EMS), You can navigate through eConf interface using this left-side menu, which provides access to different configuration panels:
- Elum Logo: Clicking on the logo will return you to the homepage of the interface.
- “Network” panel: Used to configure LAN connections, serial connections for devices,
and internet connectivity. - “Control” panel: Allows navigation through different control and monitoring options.
- “Data Forwarding” panel: Provides access to data export options, enabling
configuration for exporting data to third-party platforms or USB storage. - “All Devices” panel: Displays the status of all devices connected to the ePowerControl
and provides access to individual device data acquisition. - “Logs History” panel: Allows access to the history of logs, setpoints, and errors for system diagnostics and analysis.
- “System Settings” panel: Enables modification of various system settings and parameters.
A User can log out at any time by clicking on the logout button located in the bottom left corner of the eConf interface.

Network panel
The “Network” panel provides access to network settings, allowing users to configure and manage network interfaces.
Within the network menu, users can:
- Create or configure network interfaces (Serial or LAN)
- Add devices to a configured interface
Control Panel
For more details on configuring and using the different control parameters (PV, Genset, Grid, Breakers, etc.), please refer to the section Control Configuration.
Data Forwarding
Data forwarding manages all specific data exchange methods between the EMS and third-party solutions that do not use the Modbus gateway for data transfer. The Data Forwarding panel allows you to modify the data forwarding settings that were initially configured during commissioning.
Available data forwarding interfaces
- ePowerMonitor
- ePowerMonitor Next Gen
- Export FTP
- Export USB
- Energysoft
- QOS Energy
- Meteocontrol
In eConf, the Data Forwarding page allows you to configure connections with different interfaces. All mandatory settings are displayed, and once they are completed, data forwarding can be activated. Some advanced parameters can be modified in a configuration file.
Table 13: Data Forwarding Interface Options and Descriptions
| Interface | Description |
| ePowerMonitor | Sends all data from the Elum Data Model to the Elum asset management platform: ePowerMonitor. Activated upon subscription to ePowerMonitor |
| FTP | Allows sending data from the EMS to an FTP server. All data from the Elum Data Model is transferred. |
| USB | Enables exporting data from the EMS to a local USB key. All data from the Elum Data Model is transferred. |
| Energysoft | Sends available data from the Elum Data Model to the Energysoft platform. |
| QOS Energy | Sends available data from the Elum Data Model to the QOS Energy platform. |
| Meteocontrol | Sends available data from the Elum Data Model to the Meteocontrol platform. |
Devices
The Devices panel displays a list of all equipment connected to the ePowerControl, along with their current connection status.
By selecting a device in the “All Devices” panel, you can view its detailed live data to monitor its real-time performance and status.
The live data panel displays all accessible read and write registers for the selected device.
Some registers can be edited by clicking on the edit icon. When modifying a register, you will be prompted to enter a new value for the specific device and confirm your choice.

Logs
The Logs History panel provides access to timestamped logs of EMS events, enabling system diagnostics and analysis.
Available Log categories:
- Communication Errors: View a list of communication failures between devices.
- Device Errors: Check any device-related malfunctions detected by the system.
- Setpoints: Monitor the setpoints sent by the EMS to the plant for control operations.
Filtering and exporting Logs:
You can:
- Select a start and stop date to filter logs for a specific time range.
- Export the log data in CSV format for further analysis.
System settings
The System Settings panel allows you to access and configure essential system parameters.
Available settings:
1. Site: Enter the site name and its location details.
2. Date and Time: Define and adjust the date, time, and time zone settings.
3. Firmware: Check the installed firmware version and update if necessary.
4. Password: Change the login password for accessing eConf.
5. Advanced settings: Access additional system configurations, including logging options and factory reset.
Version
The “Firmware” panel shows the version of the Elum firmware packages installed on your ePowerControl.
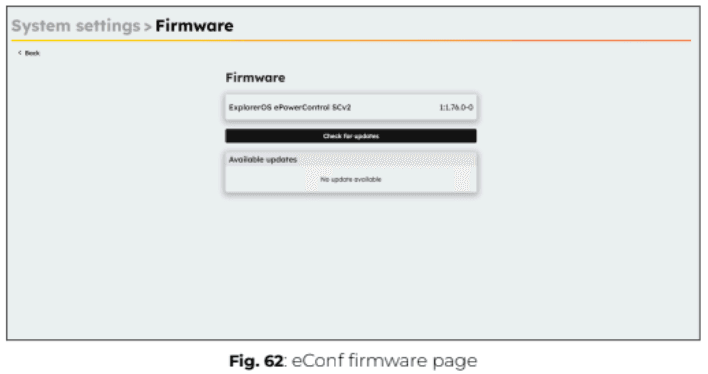
Date
The “System settings” panel allows you to access and configure the Date & Time settings, including the Timezone.
If the Explorer is connected to the internet, it will automatically synchronize with internet time via NTP. Otherwise, the time can be set manually through the interface.
The date and time settings on the controller are crucial for accurate timestamping of monitored values.
ℹ️️ Timestamps are recorded in UTC, meaning the time zone setting does not affect them. The timestamp assigned to the data corresponds to the midpoint of the reading operation. For example, if the reading starts at 12:35:30 and takes 3 seconds to complete, all variables will be assigned the timestamp 12:35:31.5.
Password
The Password panel allows you to set a new password for accessing the system.
Site
The Site panel allows you to modify the site settings, with new settings overwriting the previous ones.
Advanced
The Advanced panel allows an Advanced User to reset the ePowerControl configuration to factory settings.
⚠️ This action will permanently delete all personal data, and restoration will not be possible.
The Advanced panel also provides access to the Modbus Gateway interface of the Elum Controller. To access it, click on “Elum Technician Tools”, then select “Modbus Gateway”.
From this menu, you can select the LAN port of the Elum Explorer to be exposed for external Modbus masters to send queries. Additionally, you can configure the slave ID for each device connected to the Elum Explorer.
For more details about the Elum Modbus Gateway interface, please refer to Appendix D: Modbus Gateway.
ℹ️️ Please note that this option is only available when ordering your Elum Explorer. If you wish to subscribe to this additional feature after purchase, please contact the Elum sales team at sales@elum-energy.com.
Options and accessories
a. Cabinets
b. Antennas
c. Meters
d. UPS
e. Connectivity
f. Weather Sensors

Appendix A: New equipment driver integration by Elum
Objectives
Elum Explorers can communicate with a wide range of devices, provided they are compatible in terms of communication protocol and communication ports.
Table 14: Elum Explorers Communication Compatibility Requirements
| Communication Port | Communication Protocol |
| RS485 | Modbus RTU |
| Ethernet | Modbus TCP |
| Ethernet | SNMP v2 |
Device Integration Process
The integration process depends on the device to be integrated. Please follow instructions according to the equipment classification which new driver will be integrated by Elum.
Table 15: Critical Device Classification Criteria
| Critical when commissioning ePowerControl | Critical when commissioning ePowerControl |
| N/A | Any device of the following type: – PV Inverter |
ℹ️️ For integrating a new equipment driver into the system, you must schedule a dedicated date and time with the Elum Deployment Team. This appointment must be booked at least 10 days prior to the commissioning of the Elum Explorer to ensure smooth integration and avoid delays in deployment.
Non-critical device
To ensure a smooth integration of new devices with the Elum Explorer, follow the steps below:
1. You must send the required device documentation to Elum at least 10 days prior to the Explorer shipping date. The following documents will be requested for a new device integration:
- Datasheet
- User Manual
- Communication Protocol Technical Specification, which includes:
- Modbus Register Map (for devices communicating via Modbus RTU or Modbus TCP)
- Management Information Base (MIB) file (for devices communicating via SNMP v2)
2. Driver preparation and pre-embedding:
- The Elum Deployment Team will prepare and pre-embed the required driver(s) in your Elum Explorer before shipping.
- The Explorer will be shipped with:
- All pre-integrated drivers for already supported devices.
- Your project-specific drivers, ensuring compatibility with your system.
ℹ️️ When shipping your Elum Explorer, Elum ensures that it includes:
- All pre-integrated device drivers that are already supported by Elum.
- Project-specific drivers tailored to your system requirements.
Once the Elum Explorer has been shipped, no additional equipment drivers will be added. Ensure all necessary drivers are requested and integrated before shipping to avoid delays in commissioning.
3. Proceed with the commissioning of your Elum Explorer by setting up communication and testing the new device following the same procedure as for other connected devices.
- Once the commissioning is complete, the Elum Deployment Team will conduct:
- QA analysis to verify the integration.
- Consistency check to ensure the new driver functions correctly within the system.
ℹ️️ At the end of the commissioning process, the device must appear as “Connected” in the Overview Panel of the eConf interface.
If real-time monitored values appear inconsistent, please contact the Elum Deployment Team at support@elum-energy.com for assistance.
Once the commissioning is completed, the Elum Deployment Team operates autonomously, meaning that if a driver update is required, it can be performed remotely without requiring the presence of technical teams on-site.
ii. Critical device
1. To ensure seamless integration of new devices with the Elum Explorer, the required device manufacturer documentation must be sent to Elum at least 10 days before the Explorer shipping date.
The following documents must be provided to Elum for integration:
- Datasheet – Technical specifications of the device.
- User Manual – Instructions for installation and operation.
- Communication Protocol Technical Specification –
○ Modbus Register Map (for devices using Modbus RTU or Modbus TCP).
○ Management Information Base (MIB) File (for devices using SNMP v2).
2. The Elum Deployment Team will develop and pre-embed the required driver(s) into the Explorer before shipping.
- All previously integrated drivers, along with project-specific drivers, will be included in the shipped Explorer.
ℹ️️ When shipping your Elum Explorer, Elum ensures that it includes:
- All pre-integrated device drivers that are already supported by Elum.
- Project-specific drivers tailored to your system requirements.
Once the Elum Explorer has been shipped, no additional equipment drivers will be added. Ensure all necessary drivers are requested and integrated before shipping to avoid delays in commissioning.
3. Coordinate with the Elum Deployment Team to book a date and time for the new equipment driver integration, ensuring this is done at least 10 days before the commissioning of your Explorer.
4. Proceed with the Explorer commissioning up to Step 6: Configuring the ePowerControl on eConf. The communication setup and testing for the new device must follow the same process as other connected devices.
5. Once the setup is complete, reach out to Elum Deployment Team, which will
independently conduct additional communication tests on the driver. ⚠️ Some
adjustments in the device configuration may be required, so remain on-site
until testing is finalized. You will be notified once these tests are successfully
completed.
ℹ️️ During this phase, eConf might be temporarily unavailable while tests are being performed.
6. Proceed to the Step 7: Functional tests.
Appendix B: Ten mistakes to avoid
Table 16: Ten mistakes to avoid
| Diagnosis | Mistake | How to fix it |
| Neglected RS485 wiring | Connecting RS485 Devices
|
| Modbus communication not enabled on slave device |
| |
| Device monitoring works, but control fails. | Dynamic power control not enabled on inverter |
|
| The Elum Controller reboots when switching from On grid – Grid connected to Off grid – Genset connected mode and vice versa. | UPS wiring issue | Power Supply
|
| Breaker control fails. Wrong breaker operation. | Reverse power protection configuration issue | Refer to the Device Connection & Configuration Specific Instructions and third party documentation. Safety warnings
|
| Power meter turns off when switching between On grid – Grid connected and Off grid – Genset connected modes. | Power meters power supply wiring issue | AC Meter | 5A provided by Elum AC Meter | 333mV provided by Elum
|
| Power meter monitoring values appear incorrect or inconsistent. | Incorrect power meter VT/CT ratio | AC Meter | 5A provided by Elum When installing a Ct rAtIo, Current transformer ratio: You can obtain this ratio by dividing the primary current by the secondary current. As an example, when using 200 A to 5 A CTs, the ratio should be Vt rAtIo, Voltage transformer ratio:You can obtain this ratio by AC Meter | 333mV provided by Elum When installing a SEnSOr , CT type: As an example, when installing the power meter with Rogowski coil CTs, the type should be set to roG. Ct Prin, Current transforme Vt rAtIo, Voltage transformer ratio: You can obtain this ratio by dividing the primary voltage by the secondary voltage. As an example, when installing the power meter using no VTs, the ratio should be set to 1. |
| Power factor (Cos φ) is incorrect, but power meter readings seem fine. | Incorrect power meters VT/CT wiring | AC Meter | 5A provided by Elum AC Meter | 333mV provided by Elum
|
| Power meter values have wrong signs (positive instead of negative). | Negative power monitoring not enabled on grid meter | AC Meter | 5A provided by Elum When installing a EM330-DIN.AV5.3.H.S1.X, Carlo Gavazzi: MEASurE, Measurement type: To be set to “b” AC Meter | 333mV provided by Elum When installing a APPLiC, Measurement application: To be set to “E”. |
| No internet access (wired or cellular). | Local internet network misconfiguration or invalid SIM card contract | Configuring a wired internet Configuring a cellular internet connection Appendix C: Internet Speed Test For wired internet connections:
For cellular internet connections:
|
Appendix C: Internet Speed Test
a. Internet Speed Test Requirements for Elum Explorers
| Function of the internet access point | Max packet loss | Minimum upload rate | Minimum download rate | ePowerLog | ePowerControl SD/ZE/HFS | ePowerControl MC/PPCa |
| Firmware update | 10% | any | 50 ko/s | X | X | X |
| Data upload to Archive | 10% | 200 ko/s | – | X (ePowerMonitor) | X (ePowerMonitor) | X (ePowerMonitor) |
| Remote Commissioning or remote Assistance using SSH session | 10% | 25 ko/s | 25 ko/s | X (unstable version) | X | |
| FTP push to remote server | 10% | 50 ko/s | – | X (FTP) | X (FTP) | X (FTP) |
| Remote assistance using eConf | 10% | 200 ko/s | – | X | X | NA |
b. Test protocol to be performed
Prerequisite: disable your internet browser adblock if you have one active
1. At precise Elum controller future location, access from your mobile / computer to the following website: https://sourceforge.net/speedtest/
2. Click on the button Test now:
3. Wait for the test launch:
4. Check that the test is going to the end and take this as a screenshot (N1):
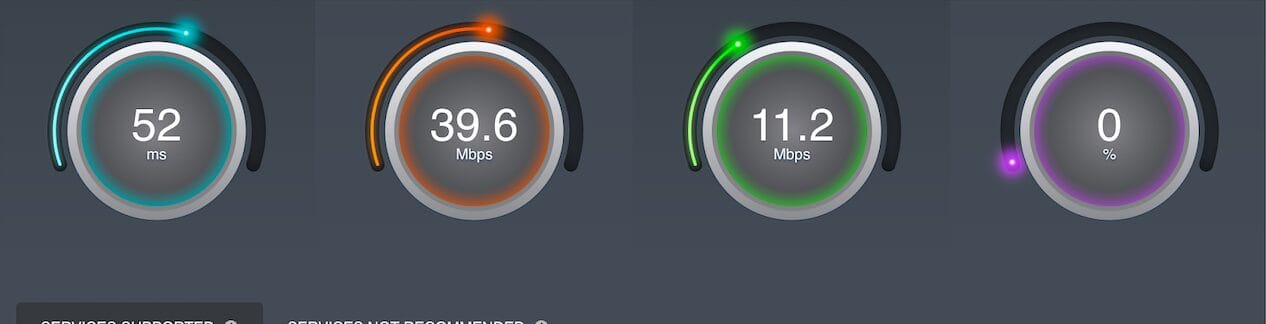
5. Once the test is complete, scroll down and click on the “view details” button:
6. Take the following 4 screenshots (N2/N3/4/N5) and send them to us:
– N2: Round Trip Time
– N3: Download Quality
– N4: Upload Quality
– N5: Internet Quality