Solar+Storage: Battery types for solar systems
Introduction
Are battery energy storage systems (BESS) the best solution to microgrid resiliency? If you’re interested in coupling solar with batteries to power your commercial or industrial buildings, read on …
We hear about them everywhere; batteries have already revolutionized several industries: from smartphones to portable computers and car industry. They now shape the future of the renewable energy industry. Batteries can now avoid high energy costs or enable you to cut the utility cord indefinitely.
Is Solar + Storage suitable for your site? For most industrial and commercial buildings equipped with a solar system and tied to a local power grid with consistent service with few, if any power outages: a battery might not be necessary. Adding solar on the existing diesel generator(s) will be enough.
However, not everyone has access to a reliable power grid. Also, for sites that have to remain off-the-grid or are totally isolated, the only solution is to rely on their own energy production system.
Adding a Solar + Storage system to your existing diesel generator(s) will not only make you less dependent on the grid but will also prevent power outages if the BESS chosen has a UPS feature. Full reliance on diesel generators could be risky in the context of volatile fuel prices therefore investing in a BESS can be the best solution. Nonetheless, this requires that your installation is equipped with an Energy Management System (EMS) such as Elum Energy ePowercontrol MC.

An EMS is a set of digital tools to monitor (e.g. ePowerMonitor, Elum’s energy monitoring software), control and optimize the power grid’s performance. All this by ensuring its proper functioning.
Your Solar + Storage (diesel) system equipped with an EMS will ensure that your system operates at the highest efficiency, saving even more on fuel costs by maximizing solar penetration.
Integrating a battery energy storage system into a solar (+ diesel) system is more challenging than it seems. Some chemistries work better in specific environments and use cases.
What types of batteries to choose?
There are multiple models of batteries capable of storing solar energy; each has advantages and disadvantages.
There are 4 types of batteries mainly used for solar energy storage applications. Understanding the differences between the 4 leading solutions available in the market will be key to selecting the right product for your project.
Below is a summary of the most trusted technologies currently on the market :
- Lithium-ion (LMO, NMC, NCA, LFP)
- Lead acid (Flooded, VRLA)
- Nickel based (NiCd)
- Flow (RFB, HFB)
Lithium-ion
Lithium-ion batteries are evolving as the electric car industry is driving their development both in technology and costs. There are 4 main lithium-ion types of battery often used for large scale solar battery storage applications :
- Lithium Manganese Oxide (LMO)
+ Fast charging
– Only recently entering the C&I market
- Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC)
+ High specific energy
– Only recently entering the C&I market
- Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide (NCA)
+ High specific energy and more stability
– Relatively new
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP)
+ long cycle life, don’t require ventilation or cooling
– Risk of thermal runaway
Those batteries have high energy density and a rather low self-discharge. They do not need prolonged priming when new; one charge is sufficient. Lithium-ion battery are in general low maintenance and a periodic discharge is not necessary.
However, most of them are still comparatively expensive to manufacture and are subject to transportation restrictions and aging, even while not being used. They also require a protection circuit to maintain voltage and current within limits.
Lead acid
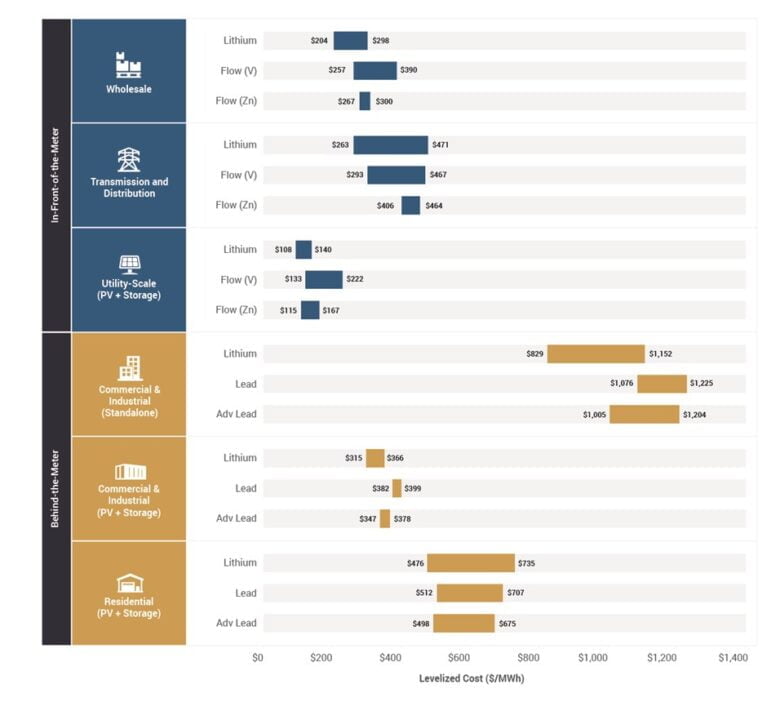
Lead acid batteries are inexpensive; their prices range between 382$ and 399$. They have the lowest self-discharge rate among this article’s rechargeable batteries. They also have high specific power and are capable of high discharge currents. However, they charge slowly (14+ hours) and have low specific energy. Their already limited cycle life can be reduced by repeated deep cycling.
Moreover, they aren’t environmentally friendly. If not properly discarded, lead acid batteries can contaminate the environment and threaten human health and nature, as their main two components are sulfuric acid and lead. Lead-acid batteries are known for being dependable and inexpensive. These batteries are heavy because of their materials and relatively inefficient in their charge and discharge compared to other batteries.
- Flooded
+ Reliable
– Requires watering, transportation restrictions, need ventilation
- Valve Regulated Lead-Acid (VRLA)
+ Valves to regulate off-gassing,little to no maintenance, can be installed in hard-to-reach applications.
– Sensitive to temperature
VRLA can be separated into two categories: absorbed glass mat (AGM) and gel. Gel performs better in warm temperatures and AGM in colder ones.
Nickel based
Nickel-based batteries have been used in large-scale energy storage projects as they perform well in all temperatures. Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) is the most common Nickel based battery technology used. They are more suitable for off-grid installation as they are a reliable backup system and don’t require regular maintenance, but lack of upkeep will reduce their cycle counts.
- Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd)
+ long cycle life, don’t require ventilation or cooling
– Risk of thermal runaway
The Nickel-Cadmium batteries are available in a wide range of sizes and performance options and can be stored in a discharged state as they have a long shelf life. They have an outstanding load performance and are not subject to regulatory control. It has to be noted that NiCd has the lowest cost per cycle in comparison to the 3 other types of battery presented.
Nevertheless, they have low specific energy compared to newer systems and high self-discharge. They are also subject to memory effects, and the low cell voltage of those batteries means that many cells are required to achieve high voltage. Besides, Cadmium is a toxic metal, making this battery type one of the least environment-friendly components with lead acid batteries.
Flow
Flow batteries are comparatively new to the battery storage market, even though the technology has been used for years. They are called flow batteries because they have a water-based solution of zinc-bromide inside them. They have greater design flexibility, thus allowing more combination between storage capacity and power output capacity.
- Redox flow batteries (RFB)
+ flexible energy storage technology
– low energy density, expensive, very large
- Hybrid flow batteries
+ flexible energy storage technology
– low charge and discharge rates, expensive, very large
Instead of adding more batteries to a storage system to increase its capacity, flow batteries only need more electrolyte liquid. This electrolyte can be replenished at any time without interrupting power output. The electrochemical cell can deliver power as long as the electrolyte solution is available.
Conclusion
Deciding on the battery storage technology will impact the whole power system use and longevity. As we have seen, lead acid batteries are more reliable and has been used for decades but they are not as flexible or efficient than the others batteries shown above.
It is definitely not easy to choose a battery storage or the right EMS that will work with it. After choosing the battery type, one need to properly size their battery fleet and find a compatible EMS. Our energy storage controller, called ePowercontrol MC, is fully compatible with most batteries on the market and will be easily integrated into your solar + storage system.


project with us?