Part 3: Off-grid - Genset Grid Forming: How to manage microgrids
Introduction:
Welcome back to our four-part series on how to effectively manage microgrids to power Commercial and Industrial buildings. Todays’ article will tackle off-grid PV diesel systems coupled with BESS and more particularly the ones that have Genset Grid Forming.
In case you missed out on our previous articles, be sure to read:
Part 1: Load Shifting for Grid-tied System and
Part 2: Solar + BESS system with Genset Backup.

Microgrids, a short recap:
Feel free to jump to the next section if you are already familiar with this concept.
A microgrid is an energy distribution network that relies on local means of producing electricity. It is designed to operate independently or in synchronization with the national grid within a defined area.
It is necessary to ensure electricity production and distribution to enable areas or buildings to secure their economic activity and benefit from reliable energy. It is also an opportunity to profit from clean distributed and renewable energy.
A microgrid can be typically composed of renewable energy sources, BESS, utility grid (when available), diesel generators, or gensets.
Depending on the grid availability two types of sites emerge; Off-grid and Grid-tied ones.
In grid-tied applications, the national DSO needs to reduce the intermittency of solar production. The battery can be seen as an alternative to provide further services for this national entity.
In off-grid applications such as; cities, islands, or mining, electricity comes mainly from thermal plants. However, fuel prices are high and uncertain due to oil price variation, logistics, and security costs. A local energy provision can be seen as a solution to solve this fuel dependency. Thus, energy suppliers tend to add solar plus storage systems to the existing gensets. We will focus on such a site in this article.
For a more in-depth discussion, here are two articles to read:
“What is a solar hybrid microgrid?”
“What is a solar diesel hybrid system?”
Microgrid controller operational mode
When the microgrid is islanded, only one energy source can be grid forming meaning that it sets the voltage and frequency of the whole grid.
In a microgrid several energy systems can be grid forming such as genset or BESS. In this article we will focus on a microgrid where the genset plant will always be the grid forming unit and the BESS and PV will be grid following.
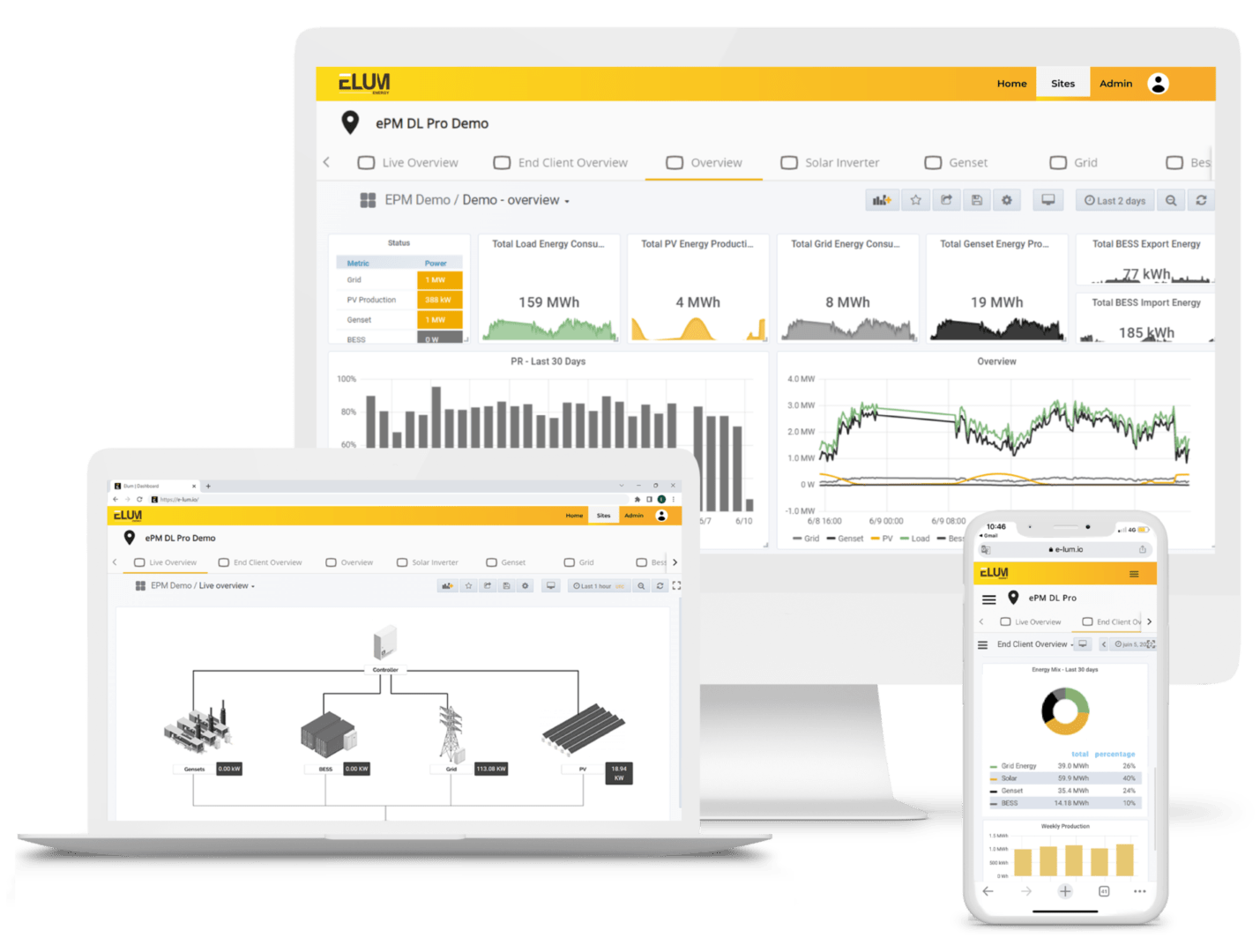
A microgrid controller is essential in coordinating these different systems to ensure seamless operation and efficiency.
As an example, you can find below one of our projects which represents the solar-diesel-BESS off grid configuration where the genset is always grid forming.

Why should you choose this configuration?
The decision on which device will be grid forming or grid following is most of the time a matter of the feature of your devices or the configuration of your project. Indeed, the nature of your on-site devices is primordial in this matter.
There are three main reasons to choose this configuration:
- In a hybrid project, genset plants are usually existing and have always formed the grid. It is therefore easier for the final client to accept an adding of PV+BESS plant without changing the grid forming unit
- The BESS can only be grid forming if its power conversion system (PCS) allows it. If the project doesn’t incorporate an advanced grid-forming power conversion system that permits the BESS to be grid forming.
- Sometimes the genset controller doesn’t allow it to be grid-following. In this case, the genset is required to be grid-forming.
- Changing the mode of the BESS can sometimes induce a blackout depending on the devices.
Additionally, the energy storage controller plays a crucial role in managing the BESS, ensuring optimal charging and discharging cycles.
the Contact us industry ?