Part 1: Load Shifting for Grid-tied Systems: How to Manage Microgrids
Introduction:

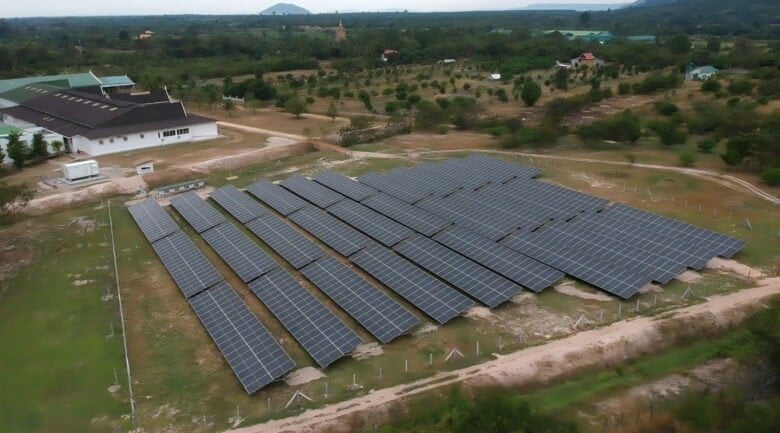
What is a microgrid?
A microgrid is an energy distribution network that relies on local means of producing electricity. It is designed to operate independently or in synchronization with the national network within a defined area. A more detailed definition can be found here: What is a solar hybrid microgrid?
Load shifting for microgrids
When used in a project with a BESS, load-shifting is a method applied during off-peak times that will lower utility expenses. Following the peak hours pricing, the battery is charged when electricity is the cheapest and discharged when it is the most expensive. Unlike many energy cost-saving strategies, load shifting tackles the “when” rather than the “how much.”
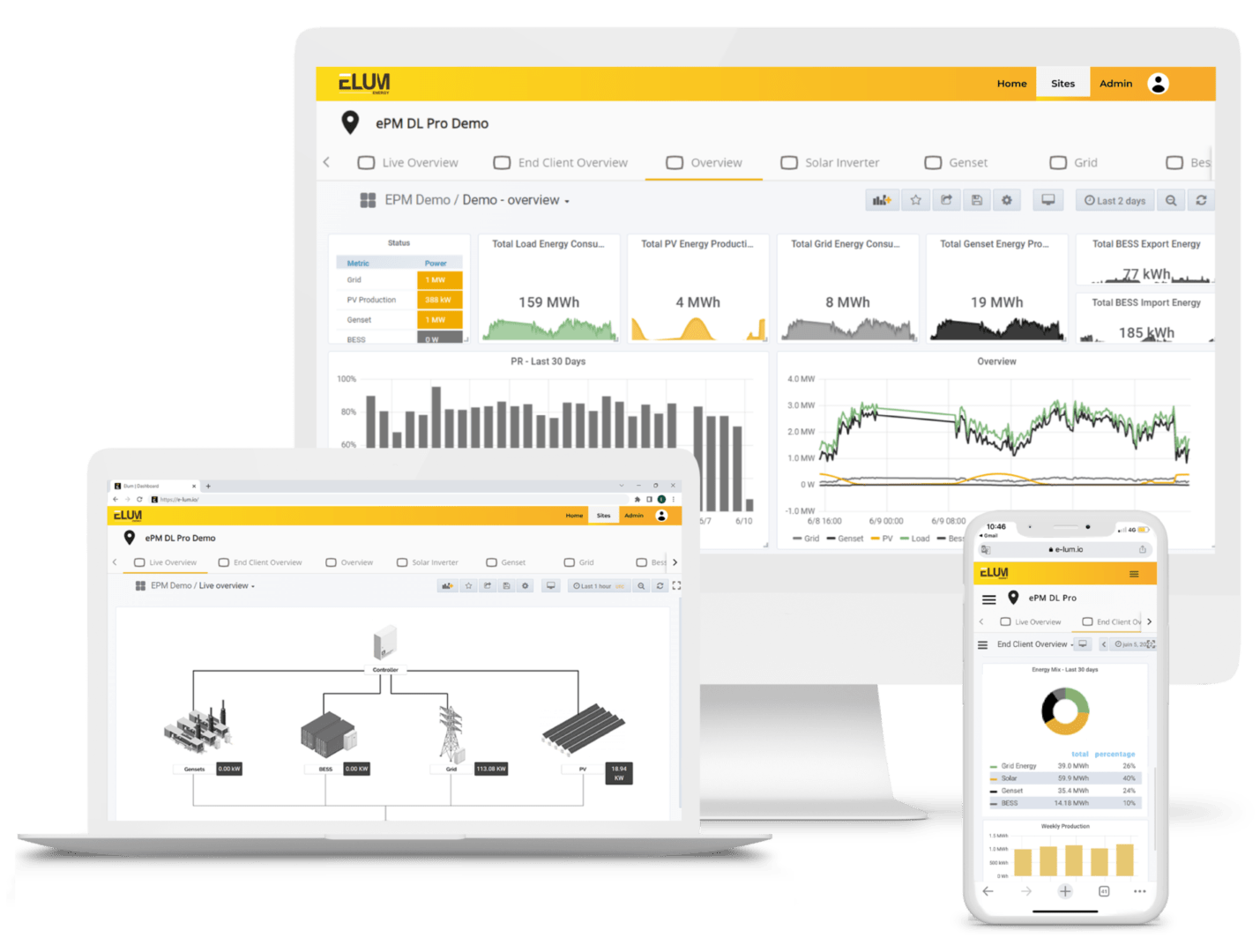
Load shifting does not reduce the quantity of energy used, but the rescheduling process allows a consequent reduction in expenses. The majority of commercial and industrial sites never operate constantly. In this case, energy demand only rises during operational hours. Charging a BESS during off-peak hours and discharging it during operational hours means peak demand charges can be significantly reduced. To be performed load shifting is best practiced when combined with a microgrid controller and an energy monitoring platform such as ePowerControl MC and ePowerMonitor.
An energy storage controller can also be utilized to enhance the management of the BESS, ensuring optimal performance and integration with other energy sources.
Microgrid controller operational mode
For load shifting applications, the operational mode is rather straightforward. The BESS can be put in two modes:
- The BESS auto consumption mode: In this mode, the BESS receives orders from the microgrid controller to either charge with the excess of the solar PV production or discharge its power to support the other units to meet the load active power demand.
- The BESS fixed charging mode: For this second mode, BESS is controlled to charge at a fixed power until a certain state of charge is reached.
The controller will orchestrate the use of the BESS to help you reduce your expenses. We recommend using ePowerControl MC and ePowerMonitor to manage your microgrids efficiently.
So, if you want to maximize your hybrid microgrid system’s profitability, contact one of our microgrid experts here.
What is the business case for this application of microgrid?
Using BESS in a microgrid only for applying a load-shifting philosophy is not economically profitable in the majority of countries. However, this load-shifting application can be reduced significantly when it is combined with other applications such as:
- Solar Maximum penetration: in some C&I applications powered with Solar, solar production can overproduce compared to the load. If BESS is installed to store the solar primarily, BESS can be also used for a load shifting application.
- Back-up application: in some C&I applications, BESS is installed to assure a backup in case of grid failure. In this case, BESS can take into account peak tariffs and off-peak tariffs to minimize the cost of purchase of electricity.
Follow on to Part 2: Solar + BESS system with Genset Backup: How to Manage Microgrods about on-grid Solar BESS genset backup applications.
the solar industry?